Targeting the Renin-angiotensin system combined with an antioxidant is highly effective in mitigating radiation-induced lung damage
- PMID: 24867538
- PMCID: PMC4146496
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2014.03.048
Targeting the Renin-angiotensin system combined with an antioxidant is highly effective in mitigating radiation-induced lung damage
Abstract
Purpose: To investigate the outcome of suppression of the renin angiotensin system using captopril combined with an antioxidant (Eukarion [EUK]-207) for mitigation of radiation-induced lung damage in rats.
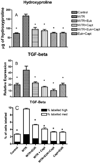
Methods and materials: The thoracic cavity of female Sprague-Dawley rats was irradiated with a single dose of 11 Gy. Treatment with captopril at a dose of 40 mg/kg/d in drinking water and EUK-207 given by subcutaneous injection (8 mg/kg daily) was started 1 week after irradiation (PI) and continuing until 14 weeks PI. Breathing rate was monitored until the rats were killed at 32 weeks PI, when lung fibrosis was assessed by lung hydroxyproline content. Lung levels of the cytokine transforming growth factor-β1 and macrophage activation were analyzed by immunohistochemistry. Oxidative DNA damage was assessed by 8-hydroxy-2-deoxyguanosine levels, and lipid peroxidation was measured by a T-BARS assay.
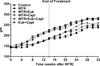
Results: The increase in breathing rate in the irradiated rats was significantly reduced by the drug treatments. The drug treatment also significantly decreased the hydroxyproline content, 8-hydroxy-2-deoxyguanosine and malondialdehyde levels, and levels of activated macrophages and the cytokine transforming growth factor-β1 at 32 weeks. Almost complete mitigation of these radiation effects was observed by combining captopril and EUK-207.
Conclusion: Captopril and EUK-207 can provide mitigation of radiation-induced lung damage out to at least 32 weeks PI after treatment given 1-14 weeks PI. Overall the combination of captopril and EUK-207 was more effective than the individual drugs used alone.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Mitigation of radiation-induced lung injury by genistein and EUK-207.Int J Radiat Biol. 2011 Aug;87(8):889-901. doi: 10.3109/09553002.2011.583315. Epub 2011 Jun 15. Int J Radiat Biol. 2011. PMID: 21675818 Free PMC article.
-
Renin-Angiotensin system suppression mitigates experimental radiation pneumonitis.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2009 Dec 1;75(5):1528-36. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2009.07.1743. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2009. PMID: 19931735 Free PMC article.
-
Mitigation of radiation-induced lung injury with EUK-207 and genistein: effects in adolescent rats.Radiat Res. 2013 Feb;179(2):125-34. doi: 10.1667/RR2954.1. Epub 2012 Dec 13. Radiat Res. 2013. PMID: 23237541 Free PMC article.
-
Short-term treatment with a SOD/catalase mimetic, EUK-207, mitigates pneumonitis and fibrosis after single-dose total-body or whole-thoracic irradiation.Radiat Res. 2012 Nov;178(5):468-80. doi: 10.1667/RR2953.1. Epub 2012 Sep 28. Radiat Res. 2012. PMID: 23020094 Free PMC article.
-
Radiation damage to the lung: mitigation by angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors.Respirology. 2012 Jan;17(1):66-71. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1843.2011.02092.x. Respirology. 2012. PMID: 22023053 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Novel Indications for Commonly Used Medications as Radiation Protectants in Spaceflight.Aerosp Med Hum Perform. 2017 Jul 1;88(7):665-676. doi: 10.3357/AMHP.4735.2017. Aerosp Med Hum Perform. 2017. PMID: 28641684 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of the renin-angiotensin system inhibitors in malignancy: a review.Am J Cancer Res. 2021 Mar 1;11(3):884-897. eCollection 2021. Am J Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 33791161 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in noninvasive imaging for detecting radiation-induced lung injury (RILI).Int J Radiat Biol. 2025 Jul 15:1-13. doi: 10.1080/09553002.2025.2531903. Online ahead of print. Int J Radiat Biol. 2025. PMID: 40663440 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitigation of Radiation-induced Pneumonitis and Lung Fibrosis using Alpha-lipoic Acid and Resveratrol.Antiinflamm Antiallergy Agents Med Chem. 2020;19(2):149-157. doi: 10.2174/1871523018666190319144020. Antiinflamm Antiallergy Agents Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 30892165 Free PMC article.
-
Development of Antioxidant COX-2 Inhibitors as Radioprotective Agents for Radiation Therapy-A Hypothesis-Driven Review.Antioxidants (Basel). 2016 Apr 19;5(2):14. doi: 10.3390/antiox5020014. Antioxidants (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27104573 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Drouet M, Herodin F. Radiation victim management and the haematologist in the future: time to revisit therapeutic guidelines? Int J Radiat Biol. 2010;86(8):636–648. - PubMed
-
- Fleckenstein K, et al. Using biological markers to predict risk of radiation injury. Semin Radiat Oncol. 2007;17(2):89–98. - PubMed
-
- Ghafoori P, et al. Radiation-induced lung injury. Assessment, management, and prevention. Oncology (Williston Park) 2008;22(1):37–47. discussion 52-3. - PubMed
-
- Hensley ML, et al. American Society of Clinical Oncology clinical practice guidelines for the use of chemotherapy and radiotherapy protectants. J Clin Oncol. 1999;17(10):3333–3355. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

