Global analysis of p53-regulated transcription identifies its direct targets and unexpected regulatory mechanisms
- PMID: 24867637
- PMCID: PMC4033189
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.02200
Global analysis of p53-regulated transcription identifies its direct targets and unexpected regulatory mechanisms
Abstract
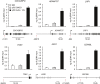
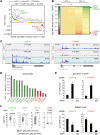
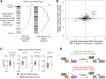
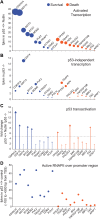
The p53 transcription factor is a potent suppressor of tumor growth. We report here an analysis of its direct transcriptional program using Global Run-On sequencing (GRO-seq). Shortly after MDM2 inhibition by Nutlin-3, low levels of p53 rapidly activate ∼200 genes, most of them not previously established as direct targets. This immediate response involves all canonical p53 effector pathways, including apoptosis. Comparative global analysis of RNA synthesis vs steady state levels revealed that microarray profiling fails to identify low abundance transcripts directly activated by p53. Interestingly, p53 represses a subset of its activation targets before MDM2 inhibition. GRO-seq uncovered a plethora of gene-specific regulatory features affecting key survival and apoptotic genes within the p53 network. p53 regulates hundreds of enhancer-derived RNAs. Strikingly, direct p53 targets harbor pre-activated enhancers highly transcribed in p53 null cells. Altogether, these results enable the study of many uncharacterized p53 target genes and unexpected regulatory mechanisms.DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.02200.001.
Keywords: PIG3; PUMA; eRNA; genomics; p21; tumor supressor.
Copyright © 2014, Allen et al.
Conflict of interest statement
JME: Reviewing editor,
The other authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures
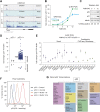
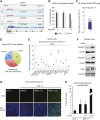
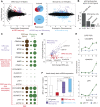
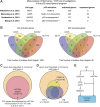

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

