Identification of receptor binding-induced conformational changes in non-visual arrestins
- PMID: 24867953
- PMCID: PMC4110305
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M114.560680
Identification of receptor binding-induced conformational changes in non-visual arrestins
Abstract
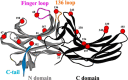
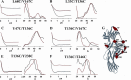
The non-visual arrestins, arrestin-2 and arrestin-3, belong to a small family of multifunctional cytosolic proteins. Non-visual arrestins interact with hundreds of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) and regulate GPCR desensitization by binding active phosphorylated GPCRs and uncoupling them from heterotrimeric G proteins. Recently, non-visual arrestins have been shown to mediate G protein-independent signaling by serving as adaptors and scaffolds that assemble multiprotein complexes. By recruiting various partners, including trafficking and signaling proteins, directly to GPCRs, non-visual arrestins connect activated receptors to diverse signaling pathways. To investigate arrestin-mediated signaling, a structural understanding of arrestin activation and interaction with GPCRs is essential. Here we identified global and local conformational changes in the non-visual arrestins upon binding to the model GPCR rhodopsin. To detect conformational changes, pairs of spin labels were introduced into arrestin-2 and arrestin-3, and the interspin distances in the absence and presence of the receptor were measured by double electron electron resonance spectroscopy. Our data indicate that both non-visual arrestins undergo several conformational changes similar to arrestin-1, including the finger loop moving toward the predicted location of the receptor in the complex as well as the C-tail release upon receptor binding. The arrestin-2 results also suggest that there is no clam shell-like closure of the N- and C-domains and that the loop containing residue 136 (homolog of 139 in arrestin-1) has high flexibility in both free and receptor-bound states.
Keywords: Arrestin; Electron Paramagnetic Resonance (EPR); G Protein-coupled Receptor (GPCR); Rhodopsin; Spectroscopy.
© 2014 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures





References
-
- Lagerström M. C., Schiöth H. B. (2008) Structural diversity of G protein-coupled receptors and significance for drug discovery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 7, 339–357 - PubMed
-
- Pierce K. L., Premont R. T., Lefkowitz R. J. (2002) Seven-transmembrane receptors. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 3, 639–650 - PubMed
-
- Lefkowitz R. J., Shenoy S. K. (2005) Transduction of receptor signals by β-arrestins. Science 308, 512–517 - PubMed
-
- Hirsch J. A., Schubert C., Gurevich V. V., Sigler P. B. (1999) A model for arrestin's regulation: the 2.8 Å crystal structure of visual arrestin. Cell 97, 257–269 - PubMed
-
- DeWire S. M., Ahn S., Lefkowitz R. J., Shenoy S. K. (2007) β-Arrestins and Cell Signaling. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 69, 483–510 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

