SAMHD1 has differential impact on the efficacies of HIV nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors
- PMID: 24867973
- PMCID: PMC4136039
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.02745-14
SAMHD1 has differential impact on the efficacies of HIV nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors
Abstract
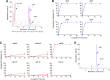
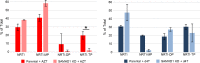
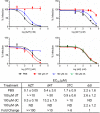
Sterile alpha motif- and histidine/aspartic acid domain-containing protein 1 (SAMHD1) limits HIV-1 replication by hydrolyzing deoxynucleoside triphosphates (dNTPs) necessary for reverse transcription. Nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs) are components of anti-HIV therapies. We report here that SAMHD1 cleaves NRTI triphosphates (TPs) at significantly lower rates than dNTPs and that SAMHD1 depletion from monocytic cells affects the susceptibility of HIV-1 infections to NRTIs in complex ways that depend not only on the relative changes in dNTP and NRTI-TP concentrations but also on the NRTI activation pathways.
Copyright © 2014, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Diamond TL, Roshal M, Jamburuthugoda VK, Reynolds HM, Merriam AR, Lee KY, Balakrishnan M, Bambara RA, Planelles V, Dewhurst S, Kim B. 2004. Macrophage tropism of HIV-1 depends on efficient cellular dNTP utilization by reverse transcriptase. J. Biol. Chem. 279:51545–51553. 10.1074/jbc.M408573200 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lahouassa H, Daddacha W, Hofmann H, Ayinde D, Logue EC, Dragin L, Bloch N, Maudet C, Bertrand M, Gramberg T, Pancino G, Priet S, Canard B, Laguette N, Benkirane M, Transy C, Landau NR, Kim B, Margottin-Goguet F. 2012. SAMHD1 restricts the replication of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 by depleting the intracellular pool of deoxynucleoside triphosphates. Nat. Immunol. 13:223–228. 10.1038/ni.2236 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baldauf HM, Pan X, Erikson E, Schmidt S, Daddacha W, Burggraf M, Schenkova K, Ambiel I, Wabnitz G, Gramberg T, Panitz S, Flory E, Landau NR, Sertel S, Rutsch F, Lasitschka F, Kim B, Konig R, Fackler OT, Keppler OT. 2012. SAMHD1 restricts HIV-1 infection in resting CD4+ T cells. Nat. Med. 18:1682–1687. 10.1038/nm.2964 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- AI100890/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- GM103368/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI079801/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI076119/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI058864/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI100890/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI099284/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P50 GM103368/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- AI058864/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R33 AI079801/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI079801/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI076119/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI099284/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI112417/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI076119/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI067059/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI112417/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

