Visual and optical performance of diffractive multifocal intraocular lenses with different haptic designs: 6 month follow-up
- PMID: 24868143
- PMCID: PMC4027939
- DOI: 10.2147/OPTH.S60493
Visual and optical performance of diffractive multifocal intraocular lenses with different haptic designs: 6 month follow-up
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate and compare the visual acuity outcomes and optical performances of eyes implanted with two diffractive multifocal intraocular lens (IOL) models with either a plate haptic design or a modified-C design.
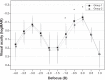
Methods: This retrospective study comprised cataract patients who were implanted with either a plate haptic multifocal IOL model (Acriva(UD) Reviol BB MFM 611 [VSY Biotechnology, Amsterdam, the Netherlands], group 1) or a modified-C haptic multifocal IOL model (Acriva(UD) Reviol BB MF 613 [VSY Biotechnology, Amsterdam, the Netherlands], group 2) between June 2012 and May 2013. The 6 month postoperative visual acuity, refraction, defocus curve, contrast sensitivity, and wave-front aberration were evaluated and compared between these eyes, using different IOL models.
Results: One hundred fifty-eight eyes of 107 patients were included in this study. Significant improvement in visual acuities and refraction was found in both groups after cataract surgery (P<0.01). The visual acuity and contrast sensitivity were statistically better in group 1 than in group 2 (P<0.01). No statistically significant difference in the corneal higher-order aberrations was found between the two groups (P>0.05). However, the ocular higher-order aberrations in group 2 were significantly greater than in group 1 (P<0.05).
Conclusion: At 6 months postoperatively, both Acriva(UD) Reviol BB MFM 611 IOL and Acriva(UD) Reviol BB MF 613 IOL achieved excellent visual and refractive outcomes. The multifocal IOL model with plate haptic design resulted in better optical performances than that with the modified-C haptic design.
Keywords: AcrivaUD; VSY; cataract surgery; modified-C haptic; multifocal intraocular lens; plate haptic.
Figures




References
-
- Ale JB. Intraocular lens tilt and decentration: a concern for contemporary IOL designs. Nepal J Ophthalmol. 2011;3(1):68–77. - PubMed
-
- Knorz MC. Multifocal intraocular lenses: overview of their capabilities, limitations, and clinical benefits. J Refract Surg. 2008;24(3):215–217. - PubMed
-
- Alió JL, Piñero DP, Plaza-Puche AB, Chan MJ. Visual outcomes and optical performance of a monofocal intraocular lens and a new-generation multifocal intraocular lens. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2011;37(2):241–250. - PubMed
-
- Lane SS, Morris M, Nordan L, Packer M, Tarantino N, Wallace RB., 3rd Multifocal intraocular lenses. Ophthalmol Clin North Am. 2006;19(1):89–105. - PubMed
-
- Alió JL, Grabner G, Plaza-Puche AB, et al. Postoperative bilateral reading performance with 4 intraocular lens models: six-month results. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2011;37(5):842–852. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

