Pulmonary hemorrhage in pediatric lupus anticoagulant hypoprothrombinemia syndrome
- PMID: 24868219
- PMCID: PMC4030123
- DOI: 10.3345/kjp.2014.57.4.202
Pulmonary hemorrhage in pediatric lupus anticoagulant hypoprothrombinemia syndrome
Abstract
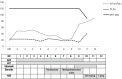
Lupus anticoagulant-hypoprothrombinemia syndrome (LAHPS), a very rare disease that is caused by the presence of antifactor II antibodies, is usually counterbalanced by the prothrombotic effect of lupus anticoagulant (LAC). Patients with LAHPS are treated using fresh frozen plasma, steroids, immunosuppressive agents, and immunoglobulins for managing the disease and controlling hemorrhages. Notably, steroids are the important treatment for treating hypoprothrombinemia and controlling the bleeding. However, some patients suffer from severe, life-threatening hemorrhages, when factor II levels remain very low in spite of treatment with steroids. Here, we report a case of LAHPS in a 15-year-old girl who experienced pulmonary hemorrhage with rapid progression. She was referred to our hospital owing to easy bruising and prolonged bleeding. She was diagnosed with LAHPS that presented with pancytopenia, positive antinuclear antibody, proloned prothrombin time, activated partial thromboplastin time, positive LAC antibody, and factor II deficiency. Her treatment included massive blood transfusion, high-dose methylprednisolone, vitamin K, and immunoglobulin. However, she died due to uncontrolled pulmonary hemorrhage.
Keywords: Immunoglobulins; Lupus anticoagulant-hypoprothrombinemia syndrome; Steroids.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
References
-
- Taddio A, Brescia AC, Lepore L, Rose' CD. Steady improvement of prothrombin levels after cyclophosphamide therapy in pediatric lupus anticoagulant hypoprothrombinemia syndrome (LAHPS) Clin Rheumatol. 2007;26:2167–2169. - PubMed
-
- Vivaldi P, Rossetti G, Galli M, Finazzi G. Severe bleeding due to acquired hypoprothrombinemia-lupus anticoagulant syndrome. Case report and review of literature. Haematologica. 1997;82:345–347. - PubMed
-
- Hift RJ, Bird AR, Sarembock BD. Acquired hypoprothrombinaemia and lupus anticoagulant: response to steroid therapy. Br J Rheumatol. 1991;30:308–310. - PubMed
-
- Male C, Lechner K, Eichinger S, Kyrle PA, Kapiotis S, Wank H, et al. Clinical significance of lupus anticoagulants in children. J Pediatr. 1999;134:199–205. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources