Achievements of Polish doctors in gastrodiaphanoscopy at the turn of the 19(th) and 20(th) centuries
- PMID: 24868282
- PMCID: PMC4027837
- DOI: 10.5114/pg.2013.39916
Achievements of Polish doctors in gastrodiaphanoscopy at the turn of the 19(th) and 20(th) centuries
Abstract
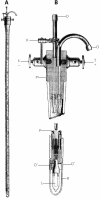
Diaphanoscopy/transillumination, the method of shining a bright light through tissues, was devised in the mid-19(th) century and developed after the invention of the light bulb by T.A. Edison. Benjamin Milliot was the first to examine the stomach by means of an incandescent platinum wire. The experiments conducted by Max Einhorn using a device consisting of a Nelaton catheter with an inserted light bulb, were valuable. In Poland the method of gastrodiaphanoscopy was popularized by Teodor Heryng, Mikołaj Rejchman and by Warsaw doctors. They used a diaphanoscope consisting of a gutta-percha probe distally equipped with a metal attachment with a light bulb hidden in it and with a so-called cooling device. The examination would usually be conducted in the standing position after the stomach had been filled with water. Light patches corresponding to the stomach's lower and side boundaries would be obtained. Rejchman's observation, that such a contractile and flexible organ as the stomach, changing its volume and position, is bound to change its light image, was correct. Heryng's and Rejchman's research inspired the foreign researchers Renvier, Leopold Kuttner and John Jacobson. Extensive research was subsequently conducted by C.A. Meltzing and Wilhelm Schwartz. Diaphanoscopy would also be performed by Walery Jaworski, the pioneer of gastrology. He was particularly interested in transillumination of the stomach, peritoneum and omentum tumours. Eugeniusz Kozierowski, a practicing physician from Gorlice, diagnosed neoplastic pylorostenosisusing this method. Gastrodiaphanoscopy is a historical method, now of no value against gastroendoscopy and the state-of-the-art methods of image diagnostics.
Keywords: gastric diagnostics; history of gastrology; history of medicine.
Figures
References
-
- Mikulicz J. Ueber Gastroskopie und Oesophagoskopie. Centralbl Chir. 1881;37:137.
-
- Diepgen P. Geschichte der Medizin. Berlin: 1955. p. 166.
-
- Karcz D, Mikulicz J. The founder of oesophagoscopy and gastroscopy [Polish] Arch Hist Med. 1977;40:327–30. - PubMed
-
- Aubinais Metroscopie. Union Medic. 1864;37:152–64.
-
- Neugebauer L. The application of magnesium light in examining the abdominal cavity [Polish] Pam Tow Lek Warsaw. 1866;55:101–2.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
