Animal models of atherosclerosis
- PMID: 24868511
- PMCID: PMC4023305
- DOI: 10.12998/wjcc.v2.i5.126
Animal models of atherosclerosis
Abstract
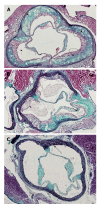
In this mini-review several commonly used animal models of atherosclerosis have been discussed. Among them, emphasis has been made on mice, rabbits, pigs and non-human primates. Although these animal models have played a significant role in our understanding of induction of atherosclerotic lesions, we still lack a reliable animal model for regression of the disease. Researchers have reported several genetically modified and transgenic animal models that replicate human atherosclerosis, however each of current animal models have some limitations. Among these animal models, the apolipoprotein (apo) E-knockout (KO) mice have been used extensively because they develop spontaneous atherosclerosis. Furthermore, atherosclerotic lesions developed in this model depending on experimental design may resemble humans' stable and unstable atherosclerotic lesions. This mouse model of hypercholesterolemia and atherosclerosis has been also used to investigate the impact of oxidative stress and inflammation on atherogenesis. Low density lipoprotein (LDL)-r-KO mice are a model of human familial hypercholesterolemia. However, unlike apo E-KO mice, the LDL-r-KO mice do not develop spontaneous atherosclerosis. Both apo E-KO and LDL-r-KO mice have been employed to generate other relevant mouse models of cardiovascular disease through breeding strategies. In addition to mice, rabbits have been used extensively particularly to understand the mechanisms of cholesterol-induced atherosclerosis. The present review paper details the characteristics of animal models that are used in atherosclerosis research.
Keywords: Animal models; Atherosclerosis; Disease; Dyslipidemia.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) 2013. Available from: http: //www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs317/en/
-
- Ignatowski AC. Influence of animal food on the organism of rabbits. S Peterb Izviest Imp Voyenno-Med Akad. 1908;16:154–173.
-
- Zhang SH, Reddick RL, Piedrahita JA, Maeda N. Spontaneous hypercholesterolemia and arterial lesions in mice lacking apolipoprotein E. Science. 1992;258:468–471. - PubMed
-
- Mezdour H, Jones R, Dengremont C, Castro G, Maeda N. Hepatic lipase deficiency increases plasma cholesterol but reduces susceptibility to atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:13570–13575. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

