N-terminus of the protein kinase CLK1 induces SR protein hyperphosphorylation
- PMID: 24869919
- PMCID: PMC5056641
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20140494
N-terminus of the protein kinase CLK1 induces SR protein hyperphosphorylation
Abstract
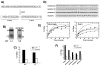
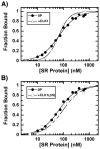
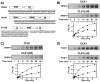
SR proteins are essential splicing factors that are regulated through multisite phosphorylation of their RS (arginine/serine-rich) domains by two major families of protein kinases. The SRPKs (SR-specific protein kinases) efficiently phosphorylate the arginine/serine dipeptides in the RS domain using a conserved docking groove in the kinase domain. In contrast, CLKs (Cdc2-like kinases) lack a docking groove and phosphorylate both arginine/serine and serine-proline dipeptides, modifications that generate a hyperphosphorylated state important for unique SR protein-dependent splicing activities. All CLKs contain long flexible N-terminal extensions (140-300 residues) that resemble the RS domains present in their substrate SR proteins. We showed that the N-terminus in CLK1 contacts both the kinase domain and the RS domain of the SR protein SRSF1 (SR protein splicing factor 1). This interaction not only is essential for facilitating hyperphosphorylation, but also induces co-operative binding of SRSF1 to RNA. The N-terminus of CLK1 enhances the total phosphoryl contents of a panel of physiological substrates including SRSF1, SRSF2, SRSF5 and Tra2β1 (transformer 2β1) by 2-3-fold. These findings suggest that CLK1-dependent hyperphosphorylation is the result of a general mechanism in which the N-terminus acts as a bridge connecting the kinase domain and the RS domain of the SR protein.
Figures

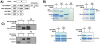

References
-
- Adams JA. Kinetic and Catalytic Mechanisms of Protein Kinases. Chemical Reviews. 2001;101:2271–2290. - PubMed
-
- Long JC, Caceres JF. The SR protein family of splicing factors: master regulators of gene expression. Biochem J. 2009;417:15–27. - PubMed
-
- Xiang S, Gapsys V, Kim HY, Bessonov S, Hsiao HH, Mohlmann S, Klaukien V, Ficner R, Becker S, Urlaub H, Luhrmann R, de Groot B, Zweckstetter M. Phosphorylation drives a dynamic switch in serine/arginine-rich proteins. Structure. 2013;21:2162–2174. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

