Role of TGF-β receptor III localization in polarity and breast cancer progression
- PMID: 24870032
- PMCID: PMC4116303
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.E14-03-0825
Role of TGF-β receptor III localization in polarity and breast cancer progression
Abstract
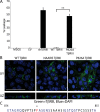
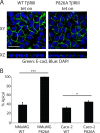
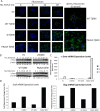
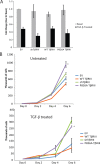
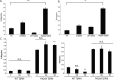
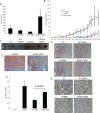
The majority of breast cancers originate from the highly polarized luminal epithelial cells lining the breast ducts. However, cell polarity is often lost during breast cancer progression. The type III transforming growth factor-β cell surface receptor (TβRIII) functions as a suppressor of breast cancer progression and also regulates the process of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT), a consequence of which is the loss of cell polarity. Many cell surface proteins exhibit polarized expression, being targeted specifically to the apical or basolateral domains. Here we demonstrate that TβRIII is basolaterally localized in polarized breast epithelial cells and that disruption of the basolateral targeting of TβRIII through a single amino acid mutation of proline 826 in the cytosolic domain results in global loss of cell polarity through enhanced EMT. In addition, the mistargeting of TβRIII results in enhanced proliferation, migration, and invasion in vitro and enhanced tumor formation and invasion in an in vivo mouse model of breast carcinoma. These results suggest that proper localization of TβRIII is critical for maintenance of epithelial cell polarity and phenotype and expand the mechanisms by which TβRIII prevents breast cancer initiation and progression.
© 2014 Meyer et al. This article is distributed by The American Society for Cell Biology under license from the author(s). Two months after publication it is available to the public under an Attribution–Noncommercial–Share Alike 3.0 Unported Creative Commons License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0).
Figures


References
-
- Aroeti B, Okhrimenko H, Reich V, Orzech E. Polarized trafficking of plasma membrane proteins: emerging roles for coats, SNAREs, GTPases and their link to the cytoskeleton. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1998;1376:57–90. - PubMed
-
- Balda MS, Matter K. Tight junctions and the regulation of gene expression. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009;1788:761–767. - PubMed
-
- Batlle E, Sancho E, Franci C, Dominguez D, Monfar M, Baulida J, Gracia De Herreros A. The transcription factor snail is a repressor of E-cadherin gene expression in epithelial tumour cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2000;2:84–89. - PubMed
-
- Bazellieres E, Assemat E, Arsanto JP, Le Bivic A, Massey-Harroche D. Crumbs proteins in epithelial morphogenesis. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed) 2009;14:2149–2169. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

