MicroRNA-29c mediates initiation of gastric carcinogenesis by directly targeting ITGB1
- PMID: 24870620
- PMCID: PMC4384419
- DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2013-306640
MicroRNA-29c mediates initiation of gastric carcinogenesis by directly targeting ITGB1
Abstract
Objective: Gastric cancer (GC) remains difficult to cure due to heterogeneity in a clinical challenge and the molecular mechanisms underlying this disease are complex and not completely understood. Accumulating evidence suggests that microRNAs (miRNAs) play an important role in GC, but the role of specific miRNAs involved in this disease remains elusive. We performed next generation sequencing (NGS)-based whole-transcriptome profiling to discover GC-specific miRNAs, followed by functional validation of results.
Design: NGS-based miRNA profiles were generated in matched pairs of GCs and adjacent normal mucosa (NM). Quantitative RT-PCR validation of miR-29c expression was performed in 274 gastric tissues, which included two cohorts of matched GC and NM specimens. Functional validation of miR-29c and its gene targets was undertaken in cell lines, as well as K19-C2mE and K19-Wnt1/C2mE transgenic mice.
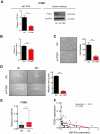
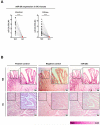
Results: NGS analysis revealed four GC-specific miRNAs. Among these, miR-29c expression was significantly decreased in GC versus NM tissues (p<0.001). Ectopic expression of miR-29c mimics in GC cell lines resulted in reduced proliferation, adhesion, invasion and migration. High miR-29c expression suppressed xenograft tumour growth in nude mice. Direct interaction between miR-29c and its newly discovered target, ITGB1, was identified in cell lines and transgenic mice. MiR-29c expression demonstrated a stepwise decrease in wild type hyperplasia-dysplasia cascade in transgenic mice models of GC.
Conclusions: MiR-29c acts as a tumour suppressor in GC by directly targeting ITGB1. Loss of miR-29c expression is an early event in the initiation of gastric carcinogenesis and may serve as a diagnostic and therapeutic biomarker for patients with GC.
Published by the BMJ Publishing Group Limited. For permission to use (where not already granted under a licence) please go to http://group.bmj.com/group/rights-licensing/permissions.
Figures





Similar articles
-
MiR-29c suppresses cell invasion and migration by directly targeting CDK6 in gastric carcinoma.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019 Sep;23(18):7920-7928. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201909_19006. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31599417
-
Interleukin 1 Up-regulates MicroRNA 135b to Promote Inflammation-Associated Gastric Carcinogenesis in Mice.Gastroenterology. 2019 Mar;156(4):1140-1155.e4. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.11.059. Epub 2018 Nov 30. Gastroenterology. 2019. PMID: 30508510
-
MiR-199a/b-3p inhibits gastric cancer cell proliferation via down-regulating PAK4/MEK/ERK signaling pathway.BMC Cancer. 2018 Jan 5;18(1):34. doi: 10.1186/s12885-017-3949-2. BMC Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29304764 Free PMC article.
-
Dysregulation of miRNAs as a signature for diagnosis and prognosis of gastric cancer and their involvement in the mechanism underlying gastric carcinogenesis and progression.IUBMB Life. 2020 May;72(5):884-898. doi: 10.1002/iub.2259. Epub 2020 Feb 20. IUBMB Life. 2020. PMID: 32078236 Review.
-
Novel Biomarkers of microRNAs in Gastric Cancer: An Overview from Diagnosis to Treatment.Microrna. 2022;11(1):12-24. doi: 10.2174/2211536611666220322160242. Microrna. 2022. PMID: 35319404 Review.
Cited by
-
miR-1301-3p Promotes Cell Proliferation and Facilitates Cell Cycle Progression via Targeting SIRT1 in Gastric Cancer.Front Oncol. 2021 Apr 27;11:664242. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.664242. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33987098 Free PMC article.
-
lncRNA/miR-29c-Mediated High Expression of LOX Can Influence the Immune Status and Chemosensitivity and Can Forecast the Poor Prognosis of Gastric Cancer.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Jan 3;9:760470. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.760470. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35047494 Free PMC article.
-
Claudins and Gastric Cancer: An Overview.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jan 7;14(2):290. doi: 10.3390/cancers14020290. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35053454 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dysregulation of non-coding RNAs in gastric cancer.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Oct 21;21(39):10956-81. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i39.10956. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 26494954 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptome analysis in primary colorectal cancer tissues from patients with and without liver metastases using next-generation sequencing.Cancer Med. 2017 Aug;6(8):1976-1987. doi: 10.1002/cam4.1147. Epub 2017 Jul 26. Cancer Med. 2017. PMID: 28745433 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2012. CA: a cancer journal for clinicians. 2012;62:10–29. - PubMed
-
- Thiel A, Ristimaki A. Gastric cancer: basic aspects. Helicobacter. 2012;17(Suppl 1):26–9. - PubMed
-
- Calin GA, Croce CM. MicroRNA signatures in human cancers. Nature reviews. Cancer. 2006;6:857–66. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
