Antiproliferative withanolides from several solanaceous species
- PMID: 24871278
- PMCID: PMC4177291
- DOI: 10.1080/14786419.2014.919286
Antiproliferative withanolides from several solanaceous species
Abstract
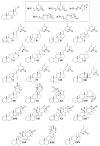
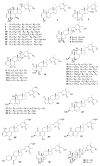
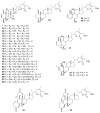
To date, our work on solanaceous species (Datura wrightii, Jaborosa caulescens, Physalis hispida, Physalis longifolia, Vassobia breviflora and Withania somnifera) has resulted in the isolation of 65 withanolides, 31 of which were new, as well as the semi-synthesis of a further 30 withanolides. Structure identification and MTS assay-based antiproliferative evaluation of these 95 compounds revealed that a Δ(2)-1-oxo functionality in ring A, in conjunction with either a 5β,6β-epoxy or 5α-chloro-6β-hydroxy moiety in ring B, is the minimum structural requirement for withanolides to produce potent cytotoxic activity. Such structure-activity relationship analysis also revealed that oxygenation (the -OH or -OR groups) at C-4, 7, 11 and 12, as well as C-14 to C-28, did not contribute towards the observed antiproliferative activity. Herein, we present a complete overview of our work as it relates to the withanolides reported from 1965 to 2013.
Keywords: Solanaceae; antiproliferative; cytotoxicity; structure–activity relationship; withanolide.
Figures

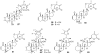
References
-
- Anjaneyulu ASR, Rao DS, Lequesne PW. Withanolides, biologically active natural steroids lactones: a review. In: Atta-ur-Rahman, editor. Studies in Natural Products Chemistry. Vol. 20. Elsevier Science, B. V.; Amsterdam: 1998. pp. 135–261.
-
- Cao CM, Zhang H, Gallagher RJ, Timmermann BN. Withanolides artifacts formed in methanol. J Nat Prod. 2013;76(11):2040–2046. - PubMed
-
- Cao CM, Zhang H, Gallagher RJ, Day VW, Kindscher K, Grogan P, Cohen MS, Timmermann BN. Withanolides from Physalis hispida. J Nat Prod. 2014;77 ASAP. - PubMed
-
- Chao CH, Chou KJ, Wen ZH, Wang GH, Wu YC, C. Dai F, Sheu JH. Paraminabeolides A-F, cytotoxic and anti-inflammatory marine withanolides from the soft coral Paraminabea acronocephala. J Nat Prod. 2011;74(5):1132–1141. - PubMed
-
- Chen LX, He H, Qiu F. Natural withanolides: an overview. Nat Prod Rep. 2011;28(4):705–740. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
