Genistein inhibits human prostate cancer cell detachment, invasion, and metastasis
- PMID: 24871471
- PMCID: PMC4144112
- DOI: 10.3945/ajcn.113.071290
Genistein inhibits human prostate cancer cell detachment, invasion, and metastasis
Abstract
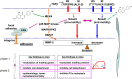
Prostate cancer (PCa) is the most commonly diagnosed cancer in men in the United States and the second leading cause of cancer death. Death is not caused by the primary tumor but rather by the formation of distinct metastatic tumors. Therefore, prevention of metastasis is of utmost importance. The natural product genistein, found in high amounts in soy products, has been implicated in preventing PCa formation and metastasis in men who consume high amounts of soy. In vitro studies and in vivo rodent models that used human PCa cells, as well as prospective human clinical trials, provide a mechanistic explanation directly supporting genistein as an antimetastatic agent. Specifically, our group showed that genistein inhibits cell detachment, protease production, cell invasion, and human PCa metastasis at concentrations achieved in humans with dietary intake. Finally, phase I and phase II clinical trials conducted by us and others showed that concentrations of genistein associated with antimetastatic efficacy in preclinical models are achievable in humans, and treatment with genistein inhibits pathways that regulate metastatic transformation in human prostate tissue.
© 2014 American Society for Nutrition.
Figures
References
-
- Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin 2013;63:11–30. - PubMed
-
- Messina M, Nagata C, Wu AH. Estimated Asian adult soy protein and isoflavone intakes. Nutr Cancer 2006;55:1–12. - PubMed
-
- Adlercreutz H, Markkanen H, Watanabe S. Plasma concentrations of phyto-oestrogens in Japanese men. Lancet 1993;342:1209–10. - PubMed
-
- Adlercreutz H. Western diet and Western diseases: some hormonal and biochemical mechanisms and associations. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl 1990;201:3–23. - PubMed
-
- Severson RK, Nomura AM, Grove JS, Stemmermann GN. A prospective study of demographics, diet, and prostate cancer among men of Japanese ancestry in Hawaii. Cancer Res 1989;49:1857–60. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

