Anti-inflammatory and antipruritic effects of luteolin from Perilla (P. frutescens L.) leaves
- PMID: 24871572
- PMCID: PMC6271665
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules19066941
Anti-inflammatory and antipruritic effects of luteolin from Perilla (P. frutescens L.) leaves
Abstract
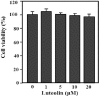
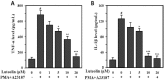
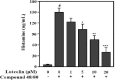
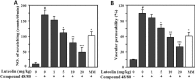
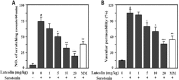
Perilla (Perilla frutescens L.) leaves have shown therapeutic efficacy in the treatment of inflammatory disorders, allergies, bronchial asthma, and systemic damage due to free radicals. In the present study we analyzed the active constituents in perilla leaves using high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and isolated luteolin, a polyphenolic flavonoid. We investigated the anti-inflammatory and antipruritic properties of luteolin. Luteolin inhibited the secretion of inflammatory cytokines such as interleukin-1β (IL-1 β) and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) from human mast cells (HMC-1) stimulated with phorbol myristate acetate plus calcium ionophore A23187 in a dose-dependent manner. Luteolin also significantly reduced the histamine release from rat peritoneal mast cells stimulated by compound 48/80, a potent histamine liberator. Furthermore, the administration of luteolin markedly inhibited the scratching behavior and vascular permeability induced by pruritogens, such as compound 48/80 or serotonin, in ICR mice. These results suggested that luteolin has potential as a therapeutic agent against inflammation and itch-related skin diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Phlomis umbrosa root inhibits mast cell-dependent allergic reactions and inflammatory cytokine secretion.Phytother Res. 2008 Feb;22(2):153-8. doi: 10.1002/ptr.2164. Phytother Res. 2008. PMID: 18167054
-
Effect of Phlomis umbrosa root on mast cell-dependent immediate-type allergic reactions by anal therapy.Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2003 Feb;25(1):73-85. doi: 10.1081/iph-120018285. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2003. PMID: 12675201
-
Anti-allergic effects of Lycopus lucidus on mast cell-mediated allergy model.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2005 Dec 15;209(3):255-62. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2005.04.011. Epub 2005 Jun 2. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2005. PMID: 15936049
-
Luteolin as a modulator of skin aging and inflammation.Biofactors. 2021 Mar;47(2):170-180. doi: 10.1002/biof.1699. Epub 2020 Dec 25. Biofactors. 2021. PMID: 33368702 Review.
-
Immunopharmacological Activities of Luteolin in Chronic Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 21;24(3):2136. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032136. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36768462 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanism of Peitu Shengjin Formula Shenlingbaizhu Powder in Treating Bronchial Asthma and Allergic Colitis through Different Diseases with Simultaneous Treatment Based on Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 May 9;2022:4687788. doi: 10.1155/2022/4687788. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 35586697 Free PMC article.
-
Luteolin-7-O-Glucuronide Improves Depression-like and Stress Coping Behaviors in Sleep Deprivation Stress Model by Activation of the BDNF Signaling.Nutrients. 2022 Aug 12;14(16):3314. doi: 10.3390/nu14163314. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36014820 Free PMC article.
-
Luteolin Relieves Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease Caused by a High-Fat Diet in Rats Through Modulating the AdipoR1/AMPK/PPARγ Signaling Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 17;26(8):3804. doi: 10.3390/ijms26083804. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40332475 Free PMC article.
-
Antioxidative and Anticancer Potential of Luteolin: A Comprehensive Approach Against Wide Range of Human Malignancies.Food Sci Nutr. 2025 Jan 19;13(1):e4682. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.4682. eCollection 2025 Jan. Food Sci Nutr. 2025. PMID: 39830909 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preparation and Evaluation of Amorphous Solid Dispersions for Enhancing Luteolin's Solubility in Simulated Saliva.Polymers (Basel). 2022 Dec 29;15(1):169. doi: 10.3390/polym15010169. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36616519 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hougee S., Sanders A., Faber J., Graus Y.M., van den Berg W.B., Garssen J., Smit H.F., Hoijer M.A. Decreased pro-inflammatory cytokine production by LPS-stimulated PBMC upon in vitro incubation with the flavonoids apigenin, luteolin or chrysin, due to selective elimination of monocytes/macrophages. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2005;69:241–248. - PubMed
-
- Kim E.K., Kim E.Y., Moon P.D., Um J.Y., Kim H.M., Lee H.S., Sohn Y., Park S.K., Jung H.S., Sohn N.W. Lithospermi radix extract inhibits histamine release and production of inflammatory cytokine in mast cells. Biosci. Biotech. Biochem. 2007;71:2886–1892. - PubMed
-
- Hosoda M., Yamaya M., Suzuki T., Yamada N., Kamanakam M., Sekizawa K., Butterfield J.H., Watanabe T., Nishimura H., Sasaki H. Effects of rhinovirus infection on histamine and cytokine production by cell lines from human mast cells and basophils. J. Immunol. 2002;169:1482–1491. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

