Prenatal exposure to hypoxia induced Beclin 1 signaling-mediated renal autophagy and altered renal development in rat fetuses
- PMID: 24872334
- PMCID: PMC4287595
- DOI: 10.1177/1933719114536474
Prenatal exposure to hypoxia induced Beclin 1 signaling-mediated renal autophagy and altered renal development in rat fetuses
Abstract
Aims: Hypoxia has adverse effects on renal development. This study was the first to test hypoxia-induced renal autophagy in rat fetuses.
Methods: Pregnant rats were exposed to hypoxia or normoxia during pregnancy and fetal kidneys were collected at gestation day 21.
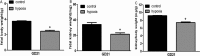
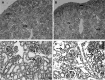
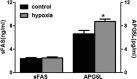
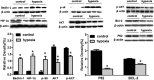
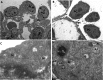
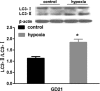
Results: Fetal kidney weight and ratio of kidney-body weight were reduced. Histological analysis showed enlargement in Bowman space and wider space between interstitia in the kidneys of fetus exposed to hypoxia. Fetal renal B-cell lymphoma 2 (BCL-2) was decreased accompanied with higher 2'-deoxyuridine 5'-triphosphate nick end-labeling staining and unchanged soluble FAS in the hypoxia group. Hypoxia increased autophagic structures, including autophagosomes and autolysosomes, in fetal kidneys and increased renal APG5L. There was an increase in renal LC3-II, Beclin 1, p-S6, hypoxia inducible factor 1α (HIF-1a), and ratio of LC3-II-LC3-I and a decrease in P62, protein kinase B (AKT), and phosphorylated AKT in the hypoxia group. Both renal mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) and Beclin 1 signaling were upregulated.
Conclusion: Hypoxia-affected fetal renal development was associated with renal apoptosis and Beclin 1 signaling-mediated autophagy.
Keywords: autophagy; hypoxia; kidney; rat fetus.
© The Author(s) 2014.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Activation of autophagy and Akt/CREB signaling play an equivalent role in the neuroprotective effect of rapamycin in neonatal hypoxia-ischemia.Autophagy. 2010 Apr;6(3):366-77. doi: 10.4161/auto.6.3.11261. Epub 2010 Apr 20. Autophagy. 2010. PMID: 20168088
-
Di-n-butyl phthalate induced hypospadias relates to autophagy in genital tubercle via the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway.J Occup Health. 2017 Jan 24;59(1):8-16. doi: 10.1539/joh.16-0089-OA. Epub 2016 Nov 22. J Occup Health. 2017. PMID: 27885243 Free PMC article.
-
Quercetin induces protective autophagy in gastric cancer cells: involvement of Akt-mTOR- and hypoxia-induced factor 1α-mediated signaling.Autophagy. 2011 Sep;7(9):966-78. doi: 10.4161/auto.7.9.15863. Epub 2011 Sep 1. Autophagy. 2011. PMID: 21610320
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) and autophagy in polycystic kidney disease (PKD).Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2011 May;300(5):F1235-43. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00348.2010. Epub 2011 Jan 26. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21270095 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia-inducible factors (HIFs) in early pregnancy: implications for miscarriage†.Biol Reprod. 2024 Nov 11;111(5):987-999. doi: 10.1093/biolre/ioae139. Biol Reprod. 2024. PMID: 39325972 Review.
Cited by
-
Autophagy and Tubular Cell Death in the Kidney.Semin Nephrol. 2016 May;36(3):174-88. doi: 10.1016/j.semnephrol.2016.03.005. Semin Nephrol. 2016. PMID: 27339383 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gestational Hypoxia and Developmental Plasticity.Physiol Rev. 2018 Jul 1;98(3):1241-1334. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00043.2017. Physiol Rev. 2018. PMID: 29717932 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deletion of the fih gene encoding an inhibitor of hypoxia-inducible factors increases hypoxia tolerance in zebrafish.J Biol Chem. 2018 Oct 5;293(40):15370-15380. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.003004. Epub 2018 Aug 20. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 30126845 Free PMC article.
-
Prenatal hypoxia increases susceptibility to kidney injury.PLoS One. 2020 Feb 21;15(2):e0229618. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0229618. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32084244 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of ion channels in regulation of acetylcholine-mediated vasoconstrictions in umbilical cords of rabbit/rats.Reprod Toxicol. 2016 Oct;65:95-103. doi: 10.1016/j.reprotox.2016.07.003. Epub 2016 Jul 13. Reprod Toxicol. 2016. PMID: 27421582 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tapanainen PJ, Bang P, Wilson K, Unterman TG, Vreman HJ, Rosenfeld RG. Maternal hypoxia as a model for intrauterine growth retardation: effects on insulin-like growth factors and their binding proteins. Pediatr Res. 1994;36(2):152–158. - PubMed
-
- Peyronnet J, Dalmaz Y, Ehrstrom M, et al. Long lasting adverse effects of prenatal hypoxia on developing autonomic nervous system and cardiovascular parameters in rats. Pflugers Arch. 2002;443(5-6):858–865. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

