An ensemble method approach to investigate kinase-specific phosphorylation sites
- PMID: 24872686
- PMCID: PMC4026567
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S57526
An ensemble method approach to investigate kinase-specific phosphorylation sites
Abstract
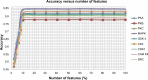
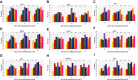
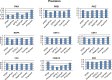
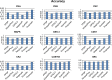
Protein phosphorylation is one of the most significant and well-studied post-translational modifications, and it plays an important role in various cellular processes. It has made a considerable impact in understanding the protein functions which are involved in revealing signal transductions and various diseases. The identification of kinase-specific phosphorylation sites has an important role in elucidating the mechanism of phosphorylation; however, experimental techniques for identifying phosphorylation sites are labor intensive and expensive. An exponentially increasing number of protein sequences generated by various laboratories across the globe require computer-aided procedures for reliably and quickly identifying the phosphorylation sites, opening a new horizon for in silico analysis. In this regard, we have introduced a novel ensemble method where we have selected three classifiers (least square support vector machine, multilayer perceptron, and k-Nearest Neighbor) and three different feature encoding parameters (dipeptide composition, physicochemical properties of amino acids, and protein-protein similarity score). Each of these classifiers is trained on each of the three different parameter systems. The final results of the ensemble method are obtained by fusing the results of all the classifiers by a weighted voting algorithm. Extensive experiments reveal that our proposed method can successfully predict phosphorylation sites in a kinase-specific manner and performs significantly better when compared with other existing phosphorylation site prediction methods.
Keywords: cell signaling; phosphate; post-translational modification.
Figures



References
-
- Salway JG. Metabolism at a Glance. 2nd edition. Oxford, UK: Blackwell Science Ltd; 1999.
-
- Matthews HR. Protein kinases and phosphatases that act on histidine, lysine, or arginine residues in eukaryotic proteins: a possible regulator of the mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade. Pharmacol Ther. 1995;67(3):323–350. - PubMed
-
- Kobayashi K, Nakano H, Hayashi M, et al. Association of phosphorylation site of tau protein with neuronal apoptosis in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurol Sci. 2003;208(1–2):17–24. - PubMed
-
- Pinna LA, Ruzzene M. How do protein kinases recognize their substrates? Biochim Biophys Acta. 1996;1314(3):191–225. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

