ChIP-less analysis of chromatin states
- PMID: 24872844
- PMCID: PMC4022240
- DOI: 10.1186/1756-8935-7-7
ChIP-less analysis of chromatin states
Abstract
Background: Histone post-translational modifications (PTMs) are key epigenetic regulators in chromatin-based processes. Increasing evidence suggests that vast combinations of PTMs exist within chromatin histones. These complex patterns, rather than individual PTMs, are thought to define functional chromatin states. However, the ability to interrogate combinatorial histone PTM patterns at the nucleosome level has been limited by the lack of direct molecular tools.
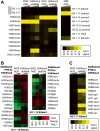
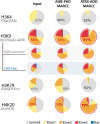
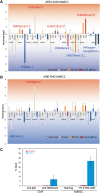
Results: Here we demonstrate an efficient, quantitative, antibody-free, chromatin immunoprecipitation-less (ChIP-less) method for interrogating diverse epigenetic states. At the heart of the workflow are recombinant chromatin reader domains, which target distinct chromatin states with combinatorial PTM patterns. Utilizing a newly designed combinatorial histone peptide microarray, we showed that three reader domains (ATRX-ADD, ING2-PHD and AIRE-PHD) displayed greater specificity towards combinatorial PTM patterns than corresponding commercial histone antibodies. Such specific recognitions were employed to develop a chromatin reader-based affinity enrichment platform (matrix-assisted reader chromatin capture, or MARCC). We successfully applied the reader-based platform to capture unique chromatin states, which were quantitatively profiled by mass spectrometry to reveal interconnections between nucleosomal histone PTMs. Specifically, a highly enriched signature that harbored H3K4me0, H3K9me2/3, H3K79me0 and H4K20me2/3 within the same nucleosome was identified from chromatin enriched by ATRX-ADD. This newly reported PTM combination was enriched in heterochromatin, as revealed by the associated DNA.
Conclusions: Our results suggest the broad utility of recombinant reader domains as an enrichment tool specific to combinatorial PTM patterns, which are difficult to probe directly by antibody-based approaches. The reader affinity platform is compatible with several downstream analyses to investigate the physical coexistence of nucleosomal PTM states associated with specific genomic loci. Collectively, the reader-based workflow will greatly facilitate our understanding of how distinct chromatin states and reader domains function in gene regulatory mechanisms.
Keywords: Affinity enrichment; Antibody-free; Chromatin; Histone; PTM; Peptide microarray; Reader domain.
Figures


References
-
- Phanstiel D, Brumbaugh J, Berggren WT, Conard K, Feng X, Levenstein ME, McAlister GC, Thomson JA, Coon JJ. Mass spectrometry identifies and quantifies 74 unique histone H4 isoforms in differentiating human embryonic stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105(11):4093–4098. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0710515105. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

