Fibrinolytic response to standardized venous occlusion in different age groups
- PMID: 2487404
- PMCID: PMC4534964
- DOI: 10.3904/kjim.1989.4.1.48
Fibrinolytic response to standardized venous occlusion in different age groups
Abstract
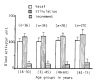
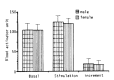
The purpose of this study was to find out the range and distribution of fibrinolytic response to standardized venous occlusion in healthy volunteers and to determine whether there were any differences according to age and sex. In 118 healthy volunteers (55 males, 63 females) of various age groups, the total fibrinolytic activity in euglobulin fractions was measured by a well controlled fibrin plate method before and after venous occlusion of 5 minutes at 100 mmHg. The difference between our method and previous methods is that we occluded for a relatively shorter duration than that of previous studies (15-20 minutes) at constant pressure (100 mmHg), instead of midway between systolic and diastolic pressure. This method was reliable and reproducible as a tool to qualify and assess the fibrinolytic activity capacity of individuals. The results showed that there was no difference in basal fibrinolytic activity and the response to stimuli in various age groups (p greater than 0.25) and in male and female groups (0.1 less than p less than 0.375).
Figures


References
-
- Charles WF, Victor JM. Physiologic regulation and pathologic disorders of fibrinolysis. Human Pathology. 1987;18:263. - PubMed
-
- Todd AS. The historical localization of fibrinolysin activator. J Path Bact. 1959;78:281. - PubMed
-
- Pandolfi M, Bjernstad A, Nilsson IM. Technical remarks on the microscopical demonstration of tissue plasminogen activator. Thromb Diath Haemorr. 1972;27:88. - PubMed
-
- Mannucci PM, Ruggeri ZM, Paretti FI, Capitanio A. 1-Deamino-8-Darginine vasopressin: A new pharmacological approach to the management of hemophilia and von Willebrand’s disease. Lancet. 1977;1:869. - PubMed
-
- Cash JD, Gader a MA, Dacosta J. The releases of plasminogen activator and Factor VIII to lysine vasopressin, arginine vasopressin in man. Brit J Haematol. 1974;27:1. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
