Interaction studies of the human and Arabidopsis thaliana Med25-ACID proteins with the herpes simplex virus VP16- and plant-specific Dreb2a transcription factors
- PMID: 24874105
- PMCID: PMC4038590
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0098575
Interaction studies of the human and Arabidopsis thaliana Med25-ACID proteins with the herpes simplex virus VP16- and plant-specific Dreb2a transcription factors
Abstract
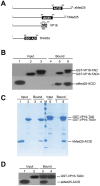
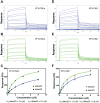
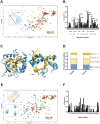
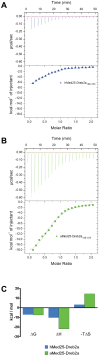
Mediator is an evolutionary conserved multi-protein complex present in all eukaryotes. It functions as a transcriptional co-regulator by conveying signals from activators and repressors to the RNA polymerase II transcription machinery. The Arabidopsis thaliana Med25 (aMed25) ACtivation Interaction Domain (ACID) interacts with the Dreb2a activator which is involved in plant stress response pathways, while Human Med25-ACID (hMed25) interacts with the herpes simplex virus VP16 activator. Despite low sequence similarity, hMed25-ACID also interacts with the plant-specific Dreb2a transcriptional activator protein. We have used GST pull-down-, surface plasmon resonance-, isothermal titration calorimetry and NMR chemical shift experiments to characterize interactions between Dreb2a and VP16, with the hMed25 and aMed25-ACIDs. We found that VP16 interacts with aMed25-ACID with similar affinity as with hMed25-ACID and that the binding surface on aMed25-ACID overlaps with the binding site for Dreb2a. We also show that the Dreb2a interaction region in hMed25-ACID overlaps with the earlier reported VP16 binding site. In addition, we show that hMed25-ACID/Dreb2a and aMed25-ACID/Dreb2a display similar binding affinities but different binding energetics. Our results therefore indicate that interaction between transcriptional regulators and their target proteins in Mediator are less dependent on the primary sequences in the interaction domains but that these domains fold into similar structures upon interaction.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Interactions between DNA, transcriptional regulator Dreb2a and the Med25 mediator subunit from Arabidopsis thaliana involve conformational changes.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Jul;40(13):5938-50. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks265. Epub 2012 Mar 24. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22447446 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and VP16 binding of the Mediator Med25 activator interaction domain.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2011 Apr;18(4):404-9. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.1997. Epub 2011 Mar 6. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21378965
-
Structure of the VP16 transactivator target in the Mediator.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2011 Apr;18(4):410-5. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.1999. Epub 2011 Mar 6. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21378963 Free PMC article.
-
The herpes simplex virus VP16-induced complex: mechanisms of combinatorial transcriptional regulation.Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1998;63:599-607. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1998.63.599. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1998. PMID: 10384325 Review. No abstract available.
-
The metazoan Mediator co-activator complex as an integrative hub for transcriptional regulation.Nat Rev Genet. 2010 Nov;11(11):761-72. doi: 10.1038/nrg2901. Epub 2010 Oct 13. Nat Rev Genet. 2010. PMID: 20940737 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Grammar rules and exceptions for the language of transcriptional activation domains.iScience. 2024 Sep 26;27(11):111057. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.111057. eCollection 2024 Nov 15. iScience. 2024. PMID: 39524347 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular switching in transcription through splicing and proline-isomerization regulates stress responses in plants.Nat Commun. 2024 Jan 18;15(1):592. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-44859-2. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38238333 Free PMC article.
-
Structural Basis for the Interaction between p53 Transactivation Domain and the Mediator Subunit MED25.Molecules. 2018 Oct 22;23(10):2726. doi: 10.3390/molecules23102726. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 30360415 Free PMC article.
-
The 9aaTAD Transactivation Domains: From Gal4 to p53.PLoS One. 2016 Sep 12;11(9):e0162842. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0162842. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27618436 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of ERM transactivation domain binding to the ACID/PTOV domain of the Mediator subunit MED25.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Aug 18;43(14):7110-21. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv650. Epub 2015 Jun 29. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 26130716 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boube M, Joulia L, Cribbs DL, Bourbon HM (2002) Evidence for a mediator of RNA polymerase II transcriptional regulation conserved from yeast to man. Cell 110: 143–151. - PubMed
-
- Bourbon HM, Aguilera A, Ansari AZ, Asturias FJ, Berk AJ, et al. (2004) A unified nomenclature for protein subunits of mediator complexes linking transcriptional regulators to RNA polymerase II. Mol Cell 14: 553–557. - PubMed
-
- Kim YJ, Bjorklund S, Li Y, Sayre MH, Kornberg RD (1994) A multiprotein mediator of transcriptional activation and its interaction with the C-terminal repeat domain of RNA polymerase II. Cell 77: 599–608. - PubMed
-
- Holstege FC, Jennings EG, Wyrick JJ, Lee TI, Hengartner CJ, et al. (1998) Dissecting the regulatory circuitry of a eukaryotic genome. Cell 95: 717–728. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

