Integrating artificial with natural cells to translate chemical messages that direct E. coli behaviour
- PMID: 24874202
- PMCID: PMC4050265
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms5012
Integrating artificial with natural cells to translate chemical messages that direct E. coli behaviour
Abstract
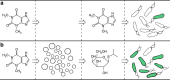
Previous efforts to control cellular behaviour have largely relied upon various forms of genetic engineering. Once the genetic content of a living cell is modified, the behaviour of that cell typically changes as well. However, other methods of cellular control are possible. All cells sense and respond to their environment. Therefore, artificial, non-living cellular mimics could be engineered to activate or repress already existing natural sensory pathways of living cells through chemical communication. Here we describe the construction of such a system. The artificial cells expand the senses of Escherichia coli by translating a chemical message that E. coli cannot sense on its own to a molecule that activates a natural cellular response. This methodology could open new opportunities in engineering cellular behaviour without exploiting genetically modified organisms.
Figures

References
-
- Mutalik V. K. et al. Precise and reliable gene expression via standard transcription and translation initiation elements. Nat. Methods 10, 354–360 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Chen Y. J. et al. Characterization of 582 natural and synthetic terminators and quantification of their design constraints. Nat. Methods 10, 659–664 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Albert R., Collins J. J. & Glass L. Introduction to focus issue: quantitative approaches to genetic networks. Chaos 23, 025001 (2013). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

