Lower expression of glutamic acid decarboxylase 67 in the prefrontal cortex in schizophrenia: contribution of altered regulation by Zif268
- PMID: 24874453
- PMCID: PMC4376371
- DOI: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2014.14010004
Lower expression of glutamic acid decarboxylase 67 in the prefrontal cortex in schizophrenia: contribution of altered regulation by Zif268
Abstract
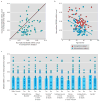
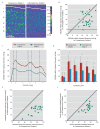
Objective: Cognitive deficits of schizophrenia may be due at least in part to lower expression of the 67-kDa isoform of glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD67), a key enzyme for GABA synthesis, in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex of individuals with schizophrenia. However, little is known about the molecular regulation of lower cortical GAD67 levels in schizophrenia. The GAD67 promoter region contains a conserved Zif268 binding site, and Zif268 activation is accompanied by increased GAD67 expression. Thus, altered expression of the immediate early gene Zif268 may contribute to lower levels of GAD67 mRNA in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in schizophrenia.
Method: The authors used polymerase chain reaction to quantify GAD67 and Zif268 mRNA levels in dorsolateral prefrontal cortex area 9 from 62 matched pairs of schizophrenia and healthy comparison subjects, and in situ hybridization to assess Zif268 expression at laminar and cellular levels of resolution. The effects of potentially confounding variables were assessed in human subjects, and the effects of antipsychotic treatments were tested in antipsychotic-exposed monkeys. The specificity of the Zif268 findings was assessed by quantifying mRNA levels for other immediate early genes.
Results: GAD67 and Zif268 mRNA levels were significantly lower and were positively correlated in the schizophrenia subjects. Both Zif268 mRNA-positive neuron density and Zif268 mRNA levels per neuron were significantly lower in the schizophrenia subjects. These findings were robust to the effects of the confounding variables examined and differed from other immediate early genes.
Conclusions: Deficient Zif268 mRNA expression may contribute to lower cortical GAD67 levels in schizophrenia, suggesting a potential mechanistic basis for altered cortical GABA synthesis and impaired cognition in schizophrenia.
Figures


Comment in
-
Identifying pathways leading to prefrontal GABA-ergic interneuron dysfunction in schizophrenia.Am J Psychiatry. 2014 Sep;171(9):906-9. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2014.14060750. Am J Psychiatry. 2014. PMID: 25178745 No abstract available.
-
Neuroinflammation versus decreased Zif268 mRNA expression as causal mediators of decreased GAD67 mRNA expression within dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in schizophrenia.Am J Psychiatry. 2014 Oct;171(10):1117-8. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2014.14060701. Am J Psychiatry. 2014. PMID: 25272348 No abstract available.
-
Response to Pearlman and Najjar.Am J Psychiatry. 2014 Oct;171(10):1118-9. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2014.14060701r. Am J Psychiatry. 2014. PMID: 25272349 No abstract available.
References
-
- Lewis DA, Hashimoto T, Volk DW. Cortical inhibitory neurons and schizophrenia. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2005;6:312–324. - PubMed
-
- Akbarian S, Kim JJ, Potkin SG, Hagman JO, Tafazzoli A, Bunney WE, Jr, Jones EG. Gene expression for glutamic acid decarboxylase is reduced without loss of neurons in prefrontal cortex of schizophrenics. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1995;52:258–266. - PubMed
-
- Duncan CE, Webster MJ, Rothmond DA, Bahn S, Elashoff M, Weickert CS. Prefrontal GABA(A) receptor alpha-subunit expression in normal postnatal human development and schizophrenia. J Psychiatr Res. 2010;44:673–681. - PubMed
-
- Thompson M, Weickert CS, Wyatt E, Webster MJ. Decreased glutamic acid decarboxylase(67) mRNA expression in multiple brain areas of patients with schizophrenia and mood disorders. J Psychiatr Res. 2009;43:970–977. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

