A new class of multimerization selective inhibitors of HIV-1 integrase
- PMID: 24874515
- PMCID: PMC4038613
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004171
A new class of multimerization selective inhibitors of HIV-1 integrase
Abstract
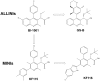
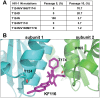
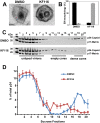
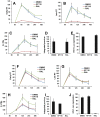
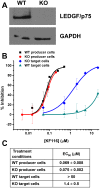
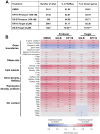
The quinoline-based allosteric HIV-1 integrase (IN) inhibitors (ALLINIs) are promising candidates for clinically useful antiviral agents. Studies using these compounds have highlighted the role of IN in both early and late stages of virus replication. However, dissecting the exact mechanism of action of the quinoline-based ALLINIs has been complicated by the multifunctional nature of these inhibitors because they both inhibit IN binding with its cofactor LEDGF/p75 and promote aberrant IN multimerization with similar potencies in vitro. Here we report design of small molecules that allowed us to probe the role of HIV-1 IN multimerization independently from IN-LEDGF/p75 interactions in infected cells. We altered the rigid quinoline moiety in ALLINIs and designed pyridine-based molecules with a rotatable single bond to allow these compounds to bridge between interacting IN subunits optimally and promote oligomerization. The most potent pyridine-based inhibitor, KF116, potently (EC50 of 0.024 µM) blocked HIV-1 replication by inducing aberrant IN multimerization in virus particles, whereas it was not effective when added to target cells. Furthermore, KF116 inhibited the HIV-1 IN variant with the A128T substitution, which confers resistance to the majority of quinoline-based ALLINIs. A genome-wide HIV-1 integration site analysis demonstrated that addition of KF116 to target or producer cells did not affect LEDGF/p75-dependent HIV-1 integration in host chromosomes, indicating that this compound is not detectably inhibiting IN-LEDGF/p75 binding. These findings delineate the significance of correctly ordered IN structure for HIV-1 particle morphogenesis and demonstrate feasibility of exploiting IN multimerization as a therapeutic target. Furthermore, pyridine-based compounds present a novel class of multimerization selective IN inhibitors as investigational probes for HIV-1 molecular biology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests. GSB was a gift from Gilead Biosciences. There are no other connections (patents, consultation, products in development etc). This does not alter our adherence to all PLoS Pathogens policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures



References
-
- Brown PO (1997) Integration. In: Coffin JM, Hughes SH, Varmus HE, editors. Retroviruses. Plainview, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory. pp. 161–204.
-
- Andrake MD, Skalka AM (1995) Multimerization determinants reside in both the catalytic core and C terminus of avian sarcoma virus integrase. J Biol Chem 270: 29299–29306. - PubMed
-
- Jenkins TM, Engelman A, Ghirlando R, Craigie R (1996) A soluble active mutant of HIV-1 integrase: involvement of both the core and carboxyl-terminal domains in multimerization. J Biol Chem 271: 7712–7718. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

