Intermittent hypercapnia enhances CO₂ responsiveness and overcomes serotonergic dysfunction
- PMID: 24874557
- PMCID: PMC4167740
- DOI: 10.1016/j.resp.2014.05.005
Intermittent hypercapnia enhances CO₂ responsiveness and overcomes serotonergic dysfunction
Abstract
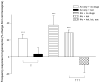
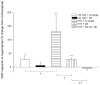
Serotonergic dysfunction compromises ventilatory chemosensitivity and may enhance vulnerability to pathologies such as the Sudden Infant Death Syndrome (SIDS). We have shown raphé contributions to central chemosensitivity involving serotonin (5-HT)-and γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-mediated mechanisms. We tested the hypothesis that mild intermittent hypercapnia (IHc) induces respiratory plasticity, due in part to strengthening of GABA mechanisms. Rat pups were IHc-pretreated (eight consecutive cycles; 5 min 5% CO2 - air, 10 min air) or constant normocapnia-pretreated as a control, each day for 5 consecutive days beginning at P12. We subsequently assessed CO2 responsiveness using the in situ perfused brainstem preparation. Hypercapnic responses were determined with and without pharmacological manipulation. Results show IHc-pretreatment induces plasticity sufficient for responsiveness despite removal of otherwise critical ketanserin-sensitive mechanisms. Responsiveness following IHc-pretreatment was absent if ketanserin was combined with GABAergic antagonism, indicating that plasticity depends on GABAergic mechanisms. We propose that IHc-induced plasticity could reduce the severity of reflex dysfunctions underlying pathologies such as SIDS.
Keywords: Chemosensitivity; GABA; Respiration; SIDS; Serotonin.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Intermittent hypercapnia-induced phrenic long-term depression is revealed after serotonin receptor blockade with methysergide in anaesthetized rats.Exp Physiol. 2016 Feb;101(2):319-31. doi: 10.1113/EP085161. Epub 2015 Dec 20. Exp Physiol. 2016. PMID: 26621042
-
Phrenic long-term depression evoked by intermittent hypercapnia is modulated by serotonergic and adrenergic receptors in raphe nuclei.J Neurophysiol. 2018 Jul 1;120(1):321-329. doi: 10.1152/jn.00776.2017. Epub 2018 Apr 4. J Neurophysiol. 2018. PMID: 29617215
-
Modulation of Serotonin and Adenosine 2A Receptors on Intermittent Hypoxia-Induced Respiratory Recovery following Mid-Cervical Contusion in the Rat.J Neurotrauma. 2019 Nov 1;36(21):2991-3004. doi: 10.1089/neu.2018.6371. Epub 2019 Jul 10. J Neurotrauma. 2019. PMID: 31099299
-
Circulatory control of phrenic motor plasticity.Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2019 Jul;265:19-23. doi: 10.1016/j.resp.2019.01.004. Epub 2019 Jan 11. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2019. PMID: 30639504 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The impact of intermittent or sustained carbon dioxide on intermittent hypoxia initiated respiratory plasticity. What is the effect of these combined stimuli on apnea severity?Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2018 Oct;256:58-66. doi: 10.1016/j.resp.2017.10.008. Epub 2017 Oct 31. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2018. PMID: 29097171 Review.
Cited by
-
CO2-inhibited neurons in the medullary raphé are GABAergic.Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2014 Nov 1;203:28-34. doi: 10.1016/j.resp.2014.07.016. Epub 2014 Aug 1. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2014. PMID: 25087734 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Awouters F. The pharmacology of ketanserin, the first selective serotonin S2-antagonist. Drug De Res. 1985;6:263–300.
-
- Bavis RW, Johnson RA, Ording KM, Otis JP, Mitchell GS. Respiratory plasticity after perinatal hypercapnia in rats. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2006;153:78–91. - PubMed
-
- Corcoran AE, Richerson GB, Harris MB. Both serotonergic and GABAergic neurons contribute to central chemosensitivity in a perfused rat brainstem. Soc Neuroscience abstracts. 2008 Online.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

