Heat shock factor HSFB2a involved in gametophyte development of Arabidopsis thaliana and its expression is controlled by a heat-inducible long non-coding antisense RNA
- PMID: 24874772
- PMCID: PMC4099531
- DOI: 10.1007/s11103-014-0202-0
Heat shock factor HSFB2a involved in gametophyte development of Arabidopsis thaliana and its expression is controlled by a heat-inducible long non-coding antisense RNA
Abstract
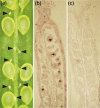
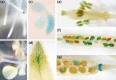
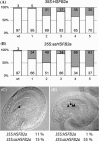
Heat stress transcription factors (HSFs) are central regulators of the heat stress response. Plant HSFs of subgroup B lack a conserved sequence motif present in the transcriptional activation domain of class A-HSFs. Arabidopsis members were found to be involved in non-heat shock functions. In the present analysis we investigated the expression, regulation and function of HSFB2a. HSFB2a expression was counteracted by a natural long non-coding antisense RNA, asHSFB2a. In leaves, the antisense RNA gene is only expressed after heat stress and dependent on the activity of HSFA1a/HSFA1b. HSFB2a and asHSFB2a RNAs were also present in the absence of heat stress in the female gametophyte. Transgenic overexpression of HSFB2a resulted in a complete knock down of the asHSFB2a expression. Conversely, asHSFB2a overexpression leads to the absence of HSFB2a RNA. The knockdown of HSFB2a by asHSFB2a correlated with an improved, knockdown of asHSFB2a by HSFB2a overexpression with an impaired biomass production early in vegetative development. In both cases the development of female gametophytes was impaired. A T-DNA knock-out line did not segregate homozygous mutant plants, only heterozygots hsfB2a-tt1/+ were viable. Approximately 50% of the female gametophytes were arrested in early development, before mitosis 3, resulting in 45% of sterile ovules. Our analysis indicates that the "Yin-Yang" regulation of gene expression at the HSFB2a locus influences vegetative and gametophytic development in Arabidopsis.
Figures

References
-
- Bechtold N, Ellis J, Pelletier G. In-planta agrobacterium-mediated gene-transfer by infiltration of adult Arabidopsis thaliana plants. Comptes Rendus De L Academie Des Sciences Serie Iii-Sciences De La Vie-Life Sciences. 1993;316:1194–1199.
-
- Begum T, Reuter R, Schöffl F (2012) Overexpression of AtHsfB4 induces specific effects on root development of Arabidopsis. Mech Dev 130:54–60 - PubMed
-
- Beisel C, Buness A, Roustan-Espinosa IM, Koch B, Schmitt S, Haas SA, Hild M, Katsuyama T, Paro R. Comparing active and repressed expression states of genes controlled by the Polycomb/Trithorax group proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2007;104:16615–16620. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0701538104. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

