Transplantation of betacellulin-transduced islets improves glucose intolerance in diabetic mice
- PMID: 24875130
- PMCID: PMC4044676
- DOI: 10.1038/emm.2014.24
Transplantation of betacellulin-transduced islets improves glucose intolerance in diabetic mice
Abstract
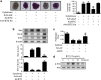
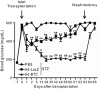
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease caused by permanent destruction of insulin-producing pancreatic β cells and requires lifelong exogenous insulin therapy. Recently, islet transplantation has been developed, and although there have been significant advances, this approach is not widely used clinically due to the poor survival rate of the engrafted islets. We hypothesized that improving survival of engrafted islets through ex vivo genetic engineering could be a novel strategy for successful islet transplantation. We transduced islets with adenoviruses expressing betacellulin, an epidermal growth factor receptor ligand, which promotes β-cell growth and differentiation, and transplanted these islets under the renal capsule of streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Transplantation with betacellulin-transduced islets resulted in prolonged normoglycemia and improved glucose tolerance compared with those of control virus-transduced islets. In addition, increased microvascular density was evident in the implanted islets, concomitant with increased endothelial von Willebrand factor immunoreactivity. Finally, cultured islets transduced with betacellulin displayed increased proliferation, reduced apoptosis and enhanced glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in the presence of cytokines. These experiments suggest that transplantation with betacellulin-transduced islets extends islet survival and preserves functional islet mass, leading to a therapeutic benefit in type 1 diabetes.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Gene therapy with neurogenin 3 and betacellulin reverses major metabolic problems in insulin-deficient diabetic mice.Endocrinology. 2009 Nov;150(11):4863-73. doi: 10.1210/en.2009-0527. Epub 2009 Oct 9. Endocrinology. 2009. PMID: 19819964 Free PMC article.
-
Functional enhancement of beta cells in transplanted pancreatic islets by secretion signal peptide-linked exendin-4 gene transduction.J Control Release. 2012 May 10;159(3):368-75. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2012.01.029. Epub 2012 Jan 27. J Control Release. 2012. PMID: 22306337
-
Betacellulin overexpression in transgenic mice improves glucose tolerance and enhances insulin secretion by isolated islets in vitro.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2009 Feb 27;299(2):188-93. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2008.11.022. Epub 2008 Nov 28. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2009. PMID: 19100309
-
Angiopoietin-1 production in islets improves islet engraftment and protects islets from cytokine-induced apoptosis.Diabetes. 2007 Sep;56(9):2274-83. doi: 10.2337/db07-0371. Epub 2007 Jun 27. Diabetes. 2007. PMID: 17596403
-
Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor enhances human islet posttransplantation survival.Transplantation. 2011 Oct 15;92(7):745-51. doi: 10.1097/TP.0b013e31822bc95a. Transplantation. 2011. PMID: 21869742 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Endothelial Cells Promote Pseudo-islet Function Through BTC-EGFR-JAK/STAT Signaling Pathways.Ann Biomed Eng. 2024 Sep;52(9):2610-2626. doi: 10.1007/s10439-024-03548-3. Epub 2024 Jun 3. Ann Biomed Eng. 2024. PMID: 38829457
-
Magnetoencapsulated human islets xenotransplanted into swine: a comparison of different transplantation sites.Xenotransplantation. 2016 May;23(3):211-21. doi: 10.1111/xen.12235. Epub 2016 May 26. Xenotransplantation. 2016. PMID: 27225644 Free PMC article.
-
Polyphenols isolated from Broussonetia kazinoki prevent cytokine-induced β-cell damage and the development of type 1 diabetes.Exp Mol Med. 2015 Apr 24;47(4):e160. doi: 10.1038/emm.2015.16. Exp Mol Med. 2015. PMID: 25907110 Free PMC article.
-
Regenerative approaches to preserve pancreatic β-cell mass and function in diabetes pathogenesis.Endocrine. 2022 Feb;75(2):338-350. doi: 10.1007/s12020-021-02941-5. Epub 2021 Nov 25. Endocrine. 2022. PMID: 34825343 Review.
-
A gelatin hydrogel nonwoven fabric improves outcomes of subcutaneous islet transplantation.Sci Rep. 2023 Jul 24;13(1):11968. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-39212-4. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37488155 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ricordi C, Strom TB. Clinical islet transplantation: advances and immunological challenges. Nat Rev Immunol. 2004;4:259–268. - PubMed
-
- Shapiro AM, Ricordi C, Hering BJ, Auchincloss H, Lindblad R, Robertson RP, et al. International trial of the Edmonton protocol for islet transplantation. New Engl J Med. 2006;355:1318–1330. - PubMed
-
- Jansson L, Carlsson PO. Graft vascular function after transplantation of pancreatic islets. Diabetologia. 2002;45:749–763. - PubMed
-
- Warnock GL, Meloche RM, Thompson D, Shapiro RJ, Fung M, Ao Z, et al. Improved human pancreatic islet isolation for a prospective cohort study of islet transplantation vs best medical therapy in type 1 diabetes mellitus. Arch Surg. 2005;140:735–744. - PubMed
-
- Westwell-Roper C, Dai DL, Soukhatcheva G, Potter KJ, van Rooijen N, Ehses JA, et al. IL-1 blockade attenuates islet amyloid polypeptide-induced proinflammatory cytokine release and pancreatic islet graft dysfunction. J Immunol. 2011;187:2755–2765. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
