Postanalytical tools improve performance of newborn screening by tandem mass spectrometry
- PMID: 24875301
- PMCID: PMC4262759
- DOI: 10.1038/gim.2014.62
Postanalytical tools improve performance of newborn screening by tandem mass spectrometry
Abstract
Purpose: The purpose of this study was to compare performance metrics of postanalytical interpretive tools of the Region 4 Stork collaborative project to the actual outcome based on cutoff values for amino acids and acylcarnitines selected by the California newborn screening program.
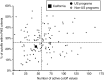
Methods: This study was a retrospective review of the outcome of 176,186 subjects born in California between 1 January and 30 June 2012. Raw data were uploaded to the Region 4 Stork Web portal as .csv files to calculate tool scores for 48 conditions simultaneously using a previously unpublished functionality, the tool runner. Scores for individual target conditions were deemed informative when equal or greater to the value representing the first percentile rank of known true-positive cases (17,099 cases in total).
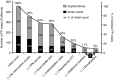
Results: In the study period, the actual false-positive rate and positive predictive value were 0.26 and 10%, respectively. Utilization of the Region 4 Stork tools, simple interpretation rules, and second-tier tests could have achieved a false-positive rate as low as 0.02% and a positive predictive value >50% by replacing the cutoff system with Region 4 Stork tools as the primary method for postanalytical interpretation.
Conclusion: Region 4 Stork interpretive tools, second-tier tests, and other evidence-based interpretation rules could have reduced false-positive cases by up to 90% in California.
Figures

References
-
- McHugh D, Cameron CA, Abdenur JE, et al. Clinical validation of cutoff target ranges in newborn screening of metabolic disorders by tandem mass spectrometry: a worldwide collaborative project. Genet Med. 2011;13:230–254. - PubMed
-
- Watson MS, Mann MY, Lloyd-Puryear MA, Rinaldo P, Howell RR. Newborn screening: toward a uniform screening panel and system [executive summary] Genet Med. 2006;8 suppl:1S–11S. - PubMed
-
- Marquardt G, Currier R, McHugh DM, et al. Enhanced interpretation of newborn screening results without analyte cutoff values. Genet Med. 2012;14:648–655. - PubMed
-
- Merritt JL, 2nd, Vedal S, Abdenur JE, et al. Infants suspected to have very-long chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency from newborn screening. Mol Genet Metab. 2014;111:484–492. - PubMed
-
- Rinaldo P, Zafari S, Tortorelli S, Matern D. Making the case for objective performance metrics in newborn screening by tandem mass spectrometry. Ment Retard Dev Disabil Res Rev. 2006;12:255–261. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

