Gene delivery from supercharged coiled-coil protein and cationic lipid hybrid complex
- PMID: 24875765
- PMCID: PMC4099184
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2014.05.005
Gene delivery from supercharged coiled-coil protein and cationic lipid hybrid complex
Abstract
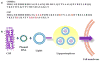
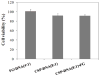
A lipoproteoplex comprised of an engineered supercharged coiled-coil protein (CSP) bearing multiple arginines and the cationic lipid formulation FuGENE HD (FG) was developed for effective condensation and delivery of nucleic acids. The CSP was able to maintain helical structure and self-assembly properties while exhibiting binding to plasmid DNA. The ternary CSP·DNA(8:1)·FG lipoproteoplex complex demonstrated enhanced transfection of β-galactosidase DNA into MC3T3-E1 mouse preosteoblasts. The lipoproteoplexes showed significant increases in transfection efficiency when compared to conventional FG and an mTat·FG lipopolyplex with a 6- and 2.5-fold increase in transfection, respectively. The CSP·DNA(8:1)·FG lipoproteoplex assembled into spherical particles with a net positive surface charge, enabling efficient gene delivery. These results support the application of lipoproteoplexes with protein engineered CSP for non-viral gene delivery.
Keywords: Cationic lipid; Coiled-coil protein; Gene delivery; Lipoproteoplexes; Supercharge.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

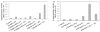

Similar articles
-
Constructing Nucleic Acid Delivering Lipoproteoplexes from Coiled-Coil Supercharged Protein and Cationic Liposomes.Methods Mol Biol. 2024;2720:191-207. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-3469-1_14. Methods Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 37775667
-
Efficient Dual siRNA and Drug Delivery Using Engineered Lipoproteoplexes.Biomacromolecules. 2017 Sep 11;18(9):2688-2698. doi: 10.1021/acs.biomac.7b00203. Epub 2017 Aug 4. Biomacromolecules. 2017. PMID: 28686014
-
Novel lipoproteoplex delivers Keap1 siRNA based gene therapy to accelerate diabetic wound healing.Biomaterials. 2017 Jul;132:1-15. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2017.04.001. Epub 2017 Apr 3. Biomaterials. 2017. PMID: 28391065
-
Improved cationic lipid formulations for in vivo gene therapy.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1995 Nov 27;772:126-39. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1995.tb44738.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1995. PMID: 8546385 Review.
-
Cationic lipid-DNA complexes for gene therapy: understanding the relationship between complex structure and gene delivery pathways at the molecular level.Curr Med Chem. 2004 Jan;11(2):133-49. doi: 10.2174/0929867043456160. Curr Med Chem. 2004. PMID: 14754413 Review.
Cited by
-
Protein Based Biomaterials for Therapeutic and Diagnostic Applications.Prog Biomed Eng (Bristol). 2022 Jan;4(1):012003. doi: 10.1088/2516-1091/ac2841. Epub 2021 Oct 26. Prog Biomed Eng (Bristol). 2022. PMID: 34950852 Free PMC article.
-
Protein-Engineered Functional Materials.Adv Healthc Mater. 2019 Jun;8(11):e1801374. doi: 10.1002/adhm.201801374. Epub 2019 Apr 2. Adv Healthc Mater. 2019. PMID: 30938924 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Constructing Nucleic Acid Delivering Lipoproteoplexes from Coiled-Coil Supercharged Protein and Cationic Liposomes.Methods Mol Biol. 2024;2720:191-207. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-3469-1_14. Methods Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 37775667
-
Emerging Landscape of Supercharged Proteins and Peptides for Drug Delivery.ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2024 Feb 21;7(3):614-629. doi: 10.1021/acsptsci.3c00397. eCollection 2024 Mar 8. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2024. PMID: 38481692 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Different-Length Hydrazone Activated Polymers for Plasmid DNA Condensation and Cellular Transfection.Biomacromolecules. 2018 Jul 9;19(7):2638-2649. doi: 10.1021/acs.biomac.8b00252. Epub 2018 Apr 26. Biomacromolecules. 2018. PMID: 29653048 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Elsabahy M, Nazarali A, Foldvari M. Non-viral nucleic acid delivery: key challenges and future directions. Curr Drug Deliv. 2011;8:235–44. - PubMed
-
- Pack DW, Hoffman AS, Pun S, Stayton PS. Design and development of polymers for gene delivery. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2005;4:581–93. - PubMed
-
- Tros de Ilarduya C, Sun Y, Duzgunes N. Gene delivery by lipoplexes and polyplexes. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2010;40:159–70. - PubMed
-
- Mah C, Byrne BJ, Flotte TR. Virus-based gene delivery systems. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2002;41:901–11. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

