Cross-talk phosphorylations by protein kinase C and Pho85p-Pho80p protein kinase regulate Pah1p phosphatidate phosphatase abundance in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- PMID: 24876385
- PMCID: PMC4081924
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M114.581462
Cross-talk phosphorylations by protein kinase C and Pho85p-Pho80p protein kinase regulate Pah1p phosphatidate phosphatase abundance in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Abstract
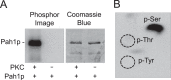
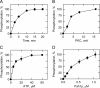
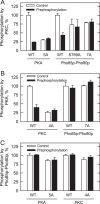
Yeast Pah1p is the phosphatidate phosphatase that catalyzes the penultimate step in triacylglycerol synthesis and plays a role in the transcriptional regulation of phospholipid synthesis genes. The enzyme is multiply phosphorylated, some of which is mediated by Pho85p-Pho80p, Cdc28p-cyclin B, and protein kinase A. Here, we showed that Pah1p is a bona fide substrate of protein kinase C; the phosphorylation reaction was time- and dose-dependent and dependent on the concentrations of ATP (Km = 4.5 μm) and Pah1p (Km = 0.75 μm). The stoichiometry of the reaction was 0.8 mol of phosphate/mol of Pah1p. By combining mass spectrometry, truncation analysis, site-directed mutagenesis, and phosphopeptide mapping, we identified Ser-677, Ser-769, Ser-773, and Ser-788 as major sites of phosphorylation. Analysis of Pah1p phosphorylations by different protein kinases showed that prephosphorylation with protein kinase C reduces its subsequent phosphorylation with protein kinase A and vice versa. Prephosphorylation with Pho85p-Pho80p had an inhibitory effect on its subsequent phosphorylation with protein kinase C; however, prephosphorylation with protein kinase C had no effect on the subsequent phosphorylation with Pho85p-Pho80p. Unlike its phosphorylations by Pho85p-Pho80p and protein kinase A, which cause a significant reduction in phosphatidate phosphatase activity, the phosphorylation of Pah1p by protein kinase C had a small stimulatory effect on the enzyme activity. Analysis of phosphorylation-deficient forms of Pah1p indicated that protein kinase C does not have a major effect on its location or its function in triacylglycerol synthesis, but instead, the phosphorylation favors loss of Pah1p abundance when it is not phosphorylated with Pho85p-Pho80p.
Keywords: Diacylglycerol; Lipid Metabolism; Phosphatase; Phosphatidate; Protein Kinase C (PKC); Triacylglycerol; Yeast.
© 2014 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Pho85p-Pho80p phosphorylation of yeast Pah1p phosphatidate phosphatase regulates its activity, location, abundance, and function in lipid metabolism.J Biol Chem. 2012 Mar 30;287(14):11290-301. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.346023. Epub 2012 Feb 9. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22334681 Free PMC article.
-
Protein kinase A-mediated phosphorylation of Pah1p phosphatidate phosphatase functions in conjunction with the Pho85p-Pho80p and Cdc28p-cyclin B kinases to regulate lipid synthesis in yeast.J Biol Chem. 2012 Sep 28;287(40):33364-76. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.402339. Epub 2012 Aug 3. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22865862 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphatidate phosphatase, a key regulator of lipid homeostasis.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Mar;1831(3):514-22. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2012.08.006. Epub 2012 Aug 14. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 22910056 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phosphorylation of Yeast Pah1 Phosphatidate Phosphatase by Casein Kinase II Regulates Its Function in Lipid Metabolism.J Biol Chem. 2016 May 6;291(19):9974-90. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.726588. Epub 2016 Apr 4. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27044741 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation-mediated regulation of the Nem1-Spo7/Pah1 phosphatase cascade in yeast lipid synthesis.Adv Biol Regul. 2022 May;84:100889. doi: 10.1016/j.jbior.2022.100889. Epub 2022 Feb 23. Adv Biol Regul. 2022. PMID: 35231723 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Lipid biosynthesis in yeasts: A comparison of the lipid biosynthetic pathway between the model nonoleaginous yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae and the model oleaginous yeast Yarrowia lipolytica.Eng Life Sci. 2016 Jul 7;17(3):292-302. doi: 10.1002/elsc.201600040. eCollection 2017 Mar. Eng Life Sci. 2016. PMID: 32624775 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A review of phosphatidate phosphatase assays.J Lipid Res. 2020 Dec;61(12):1556-1564. doi: 10.1194/jlr.R120001092. Epub 2020 Sep 22. J Lipid Res. 2020. PMID: 32963036 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Casein kinase II-mediated phosphorylation of lipin 1β phosphatidate phosphatase at Ser-285 and Ser-287 regulates its interaction with 14-3-3β protein.J Biol Chem. 2019 Feb 15;294(7):2365-2374. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.007246. Epub 2019 Jan 7. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 30617183 Free PMC article.
-
The Spo7 sequence LLI is required for Nem1-Spo7/Pah1 phosphatase cascade function in yeast lipid metabolism.J Biol Chem. 2020 Aug 14;295(33):11473-11485. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.014129. Epub 2020 Jun 11. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32527729 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation of lipid metabolic enzymes by yeast protein kinase C requires phosphatidylserine and diacylglycerol.J Lipid Res. 2017 Apr;58(4):742-751. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M075036. Epub 2017 Feb 2. J Lipid Res. 2017. PMID: 28154205 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Smith S. W., Weiss S. B., Kennedy E. P. (1957) The enzymatic dephosphorylation of phosphatidic acids. J. Biol. Chem. 228, 915–922 - PubMed
-
- Kennedy E. P. (1961) Biosynthesis of complex lipids. Fed. Proc. 20, 934–940 - PubMed
-
- Han G.-S., Siniossoglou S., Carman G. M. (2007) The cellular functions of the yeast lipin homolog Pah1p are dependent on its phosphatidate phosphatase activity. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 37026–37035 - PubMed
-
- Koonin E. V., Tatusov R. L. (1994) Computer analysis of bacterial haloacid dehalogenases defines a large superfamily of hydrolases with diverse specificity. Application of an iterative approach to database search. J. Mol. Biol. 244, 125–132 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

