A comparative effectiveness analysis of three continuous glucose monitors: the Navigator, G4 Platinum, and Enlite
- PMID: 24876423
- PMCID: PMC4764229
- DOI: 10.1177/1932296814532203
A comparative effectiveness analysis of three continuous glucose monitors: the Navigator, G4 Platinum, and Enlite
Abstract
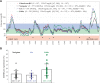
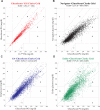
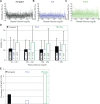
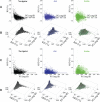
The effectiveness and safety of continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) is dependent on their accuracy and reliability. The objective of this study was to compare 3 CGMs in adult and pediatric subjects with type 1 diabetes under closed-loop blood-glucose (BG) control. Twenty-four subjects (12 adults) with type 1 diabetes each participated in one 48-hour closed-loop BG control experiment. Venous plasma glucose (PG) measurements obtained every 15 minutes (4657 values) were paired in time with corresponding CGM glucose (CGMG) measurements obtained from 3 CGMs (FreeStyle Navigator, Abbott Diabetes Care; G4 Platinum, Dexcom; Enlite, Medtronic) worn simultaneously by each subject. The Navigator and G4 Platinum (G4) had the best overall accuracy, with an aggregate mean absolute relative difference (MARD) of all paired points of 12.3 ± 12.1% and 10.8 ± 9.9%, respectively. Both had lower MARDs of all paired points than Enlite (17.9 ± 15.8%, P < .005). Very large errors (MARD > 50%) were less common with the G4 (0.5%) than with the Enlite (4.3%, P = .0001) while the number of very large errors with the Navigator (1.4%) was intermediate between the G4 and Enlite (P = .1 and P = .06, respectively). The average MARD for experiments in adolescent subjects were lower than in adult subjects for the Navigator and G4, while there was no difference for Enlite. All 3 devices had similar reliability. A comprehensive head-to-head-to-head comparison of 3 CGMs revealed marked differences in both accuracy and precision. The Navigator and G4 were found to outperform the Enlite in these areas.
Keywords: CGM; accuracy; blood glucose; blood glucose meter; continuous glucose monitoring; reliability.
© 2014 Diabetes Technology Society.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

