Passive Diffusion of Transdermal Glucose: Noninvasive Glucose Sensing Using a Fluorescent Glucose Binding Protein
- PMID: 24876581
- PMCID: PMC4455416
- DOI: 10.1177/1932296813519994
Passive Diffusion of Transdermal Glucose: Noninvasive Glucose Sensing Using a Fluorescent Glucose Binding Protein
Abstract
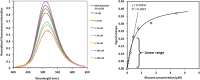
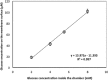
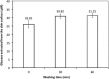
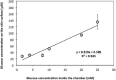
The motivation for this study was to determine if a statistically significant correlation exists between blood glucose (BG) and transdermal glucose (TG) collected by passive diffusion. A positive outcome will indicate that noninvasive passive TG diffusion is a painless alternative to collecting blood through a break on the skin. Sampling involves placing a small volume of buffer solution on the surface of membrane or skin for 5 minutes. The sample is then assayed with fluorescent GBP. In vitro testing was done on regenerated cellulose and a porcine skin model to determine diffusion of standard glucose solutions. In vivo testing was done on a healthy subject and a subject with type 2 diabetes. Glucose diffused readily through the regenerated cellulose membrane with good correlation between surface and internal glucose concentrations (R 2 = .997). But the porcine skin model required a surface prewash to achieve the same good correlation R 2 = .943). Based on this, an optimum prewash step was determined for the in vivo studies. The resulting correlation coefficients between TG and BG after a 15-minute prewash in a healthy subject and type 2 subject were .87 and .93, respectively. Removal of the extraneous glucose in the skin by prewashing was an important step in achieving good correlation between TG and BG. The results suggest that passive collection of TG is a noninvasive alternative to current practice of breaking the skin. Further studies are under way to determine the lag time between TG and BG and for the sampling protocol to be more amenable to point-of-care application.
Keywords: fluorescent glucose binding protein; noninvasive glucose sensing.
© 2014 Diabetes Technology Society.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures






References
-
- Ciudin A, Hernandez C, Simo R. Noninvasive methods of glucose measurement: current status and future perspectives. Current Diabetes. 2012;8:48-54. - PubMed
-
- Menzie M. Transdermal continuous glucose monitoring: a needle-free alternative to invasive sensors. Paper presented at: 12th Annual Diabetes Technology Meeting; 2012.
-
- Cunningham DD, Young DF. Measurements of glucose on the skin surface, in stratum corneum and in transcutaneous extracts: implications for physiological sampling. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2003;41:1224-1228. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

