An integrated multivariable artificial pancreas control system
- PMID: 24876613
- PMCID: PMC4455451
- DOI: 10.1177/1932296814524862
An integrated multivariable artificial pancreas control system
Abstract
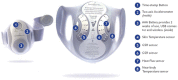
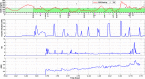
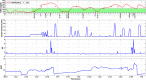
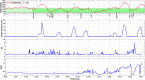
The objective was to develop a closed-loop (CL) artificial pancreas (AP) control system that uses continuous measurements of glucose concentration and physiological variables, integrated with a hypoglycemia early alarm module to regulate glucose concentration and prevent hypoglycemia. Eleven open-loop (OL) and 9 CL experiments were performed. A multivariable adaptive artificial pancreas (MAAP) system was used for the first 6 CL experiments. An integrated multivariable adaptive artificial pancreas (IMAAP) system consisting of MAAP augmented with a hypoglycemia early alarm system was used during the last 3 CL experiments. Glucose values and physical activity information were measured and transferred to the controller every 10 minutes and insulin suggestions were entered to the pump manually. All experiments were designed to be close to real-life conditions. Severe hypoglycemic episodes were seen several times during the OL experiments. With the MAAP system, the occurrence of severe hypoglycemia was decreased significantly (P < .01). No hypoglycemia was seen with the IMAAP system. There was also a significant difference (P < .01) between OL and CL experiments with regard to percentage of glucose concentration (54% vs 58%) that remained within target range (70-180 mg/dl). Integration of an adaptive control and hypoglycemia early alarm system was able to keep glucose concentration values in target range in patients with type 1 diabetes. Postprandial hypoglycemia and exercise-induced hypoglycemia did not occur when this system was used. Physical activity information improved estimation of the blood glucose concentration and effectiveness of the control system.
Keywords: adaptive control; closed-loop; hypoglycemia; type 1 diabetes.
© 2014 Diabetes Technology Society.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Steil GM, et al. Feasibility of automating insulin delivery for the treatment of type 1 diabetes. Diabetes. 2006;55(12):3344-3350. - PubMed
-
- Schaller HC, et al. On-line adaptive algorithm with glucose prediction capacity for subcutaneous closed loop control of glucose: evaluation under fasting conditions in patients with Type 1 diabetes. Diabet Med. 2006;23(1):90-93. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

