ADAMTS-12: a multifaced metalloproteinase in arthritis and inflammation
- PMID: 24876675
- PMCID: PMC4020202
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/649718
ADAMTS-12: a multifaced metalloproteinase in arthritis and inflammation
Abstract
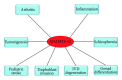
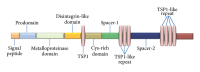
ADAMTS-12 is a member of a disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs (ADAMTS) family of proteases, which were known to play important roles in various biological and pathological processes, such as development, angiogenesis, inflammation, cancer, arthritis, and atherosclerosis. In this review, we briefly summarize the structural organization of ADAMTS-12; concentrate on the emerging role of ADAMTS-12 in several pathophysiological conditions, including intervertebral disc degeneration, tumorigenesis and angioinhibitory effects, pediatric stroke, gonad differentiation, trophoblast invasion, and genetic linkage to schizophrenia and asthma, with special focus on its role in arthritis and inflammation; and end with the perspective research of ADAMTS-12 and its potential as a promising diagnostic and therapeutic target in various kinds of diseases and conditions.
Figures


Similar articles
-
ADAMTS-18: a metalloproteinase with multiple functions.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2014 Jun 1;19(8):1456-67. doi: 10.2741/4296. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2014. PMID: 24896365 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of ADAMTSs in arthritis.Protein Cell. 2010 Jan;1(1):33-47. doi: 10.1007/s13238-010-0002-5. Epub 2010 Feb 7. Protein Cell. 2010. PMID: 21203996 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The roles of ADAMTS metalloproteinases in tumorigenesis and metastasis.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2011 Jan 1;16(5):1861-72. doi: 10.2741/3827. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2011. PMID: 21196270 Review.
-
ADAMTS proteinases: a multi-domain, multi-functional family with roles in extracellular matrix turnover and arthritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2005;7(4):160-9. doi: 10.1186/ar1783. Epub 2005 Jun 21. Arthritis Res Ther. 2005. PMID: 15987500 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Function and Roles of ADAMTS-7 in Inflammatory Diseases.Mediators Inflamm. 2015;2015:801546. doi: 10.1155/2015/801546. Epub 2015 Nov 30. Mediators Inflamm. 2015. PMID: 26696755 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Wnt and RUNX2 mediate cartilage breakdown by osteoarthritis synovial fibroblast-derived ADAMTS-7 and -12.J Cell Mol Med. 2019 Jun;23(6):3974-3983. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.14283. Epub 2019 Mar 22. J Cell Mol Med. 2019. PMID: 30903650 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic regulatory mechanism of ADAMTS12 expression in osteoarthritis.Mol Med. 2023 Jul 3;29(1):86. doi: 10.1186/s10020-023-00661-2. Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 37400752 Free PMC article.
-
Role of ADAMTS-12 in Protecting Against Inflammatory Arthritis in Mice By Interacting With and Inactivating Proinflammatory Connective Tissue Growth Factor.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018 Nov;70(11):1745-1756. doi: 10.1002/art.40552. Epub 2018 Sep 24. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018. PMID: 29750395 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular osmolarity regulates matrix homeostasis in the intervertebral disc and articular cartilage: evolving role of TonEBP.Matrix Biol. 2014 Nov;40:10-6. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2014.08.014. Epub 2014 Aug 27. Matrix Biol. 2014. PMID: 25172826 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular matrix proteomics in schizophrenia and Alzheimer's disease.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2017 Jan;409(2):379-394. doi: 10.1007/s00216-016-9900-6. Epub 2016 Sep 6. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2017. PMID: 27601046 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Levy GG, Nichols WC, Lian EC, et al. Mutations in a member of the ADAMTS gene family cause thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Nature. 2001;413(6855):488–494. - PubMed
-
- Barreda DR, Hanington PC, Walsh CK, Wong P, Belosevic M. Differentially expressed genes that encode potential markers of goldfish macrophage development in vitro. Developmental and Comparative Immunology. 2004;28(7-8):727–746. - PubMed
-
- Llamazares M, Obaya AJ, Moncada-Pazos A, et al. The ADAMTS12 metalloproteinase exhibits anti-tumorigenic properties through modulation of the Ras-dependent ERK signalling pathway. Journal of Cell Science. 2007;120(20):3544–3552. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

