Investigation of the Chemical Changes from Crude and Processed Paeoniae Radix Alba-Atractylodis Macrocephalae Rhizoma Herbal Pair Extracts by Using Q Exactive High-Performance Benchtop Quadrupole-Orbitrap LC-MS/MS
- PMID: 24876867
- PMCID: PMC4024421
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/170959
Investigation of the Chemical Changes from Crude and Processed Paeoniae Radix Alba-Atractylodis Macrocephalae Rhizoma Herbal Pair Extracts by Using Q Exactive High-Performance Benchtop Quadrupole-Orbitrap LC-MS/MS
Abstract
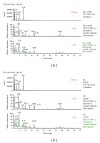
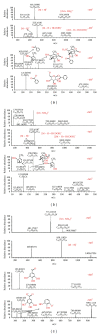
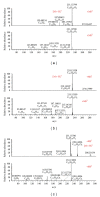
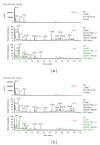
The Paeoniae Radix Alba-Atractylodis Macrocephalae Rhizoma herbal pair is mainly used for regulating the functions of liver and spleen, benefiting qi, and nourishing blood. However, the bioactive compounds for the pharmacological activities of the crude and processed Paeoniae Radix Alba-Atractylodis Macrocephalae Rhizoma herbal pair extracts are still unclear to date. In the present study, Q Exactive high-performance benchtop quadrupole-Orbitrap LC-MS/MS was applied to identify the complicated components from crude and processed Paeoniae Radix Alba, crude and processed Atractylodis Macrocephalae Rhizoma, and their crude and processed herbal pair extracts. 123 and 101 compounds were identified in crude and processed Paeoniae Radix Alba samples, respectively. Meanwhile, 32 and 26 compounds were identified in crude and processed Atractylodis Macrocephalae Rhizoma samples, respectively. In the crude and processed Paeoniae Radix Alba-Atractylodis Macrocephalae Rhizoma herbal pair extracts, co-decoction could significantly change the chemical composition of Paeoniae Radix Alba and Atractylodis Macrocephalae Rhizoma in solution. The developed method may provide a scientific foundation for deeply elucidating the processing and compatibility mechanism of Paeoniae Radix Alba and Atractylodis Macrocephalae Rhizoma.
Figures

References
-
- Qin KM, Shu YC, Cao G, et al. Thoughts and methods of Chinese materia medica processing—taking research on Rehmanniae Radix processing as an example. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs. 2013;44(11):1363–1370.
-
- Qin KM, Zheng LJ, Cao G, et al. Ideas and methods for mechanism research of traditional Chinese medicine processing—taking coffee beans roasting mechanism research as an example. Scientia Sinica Chimica. 2013;43(7):829–839.
-
- Li SL, Lai SF, Song JZ, et al. Decocting-induced chemical transformations and global quality of Du-Shen-Tang, the decoction of ginseng evaluated by UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS based chemical profiling approach. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis. 2010;53(4):946–957. - PubMed
-
- Wang C, Wang YG, Liang QD, Rang WQ, Xiao CR, Gao Y. Analysis of chemical composition in combination of Aconitum and Fritillaria by UPLC/Q-TOFMS with multivariate statistical analysis. Acta Chimica Sinica. 2011;69(16):1920–1928.
-
- Ma ZC, Zhou SS, Liang QD, et al. UPLC-TOF/MS based chemical profiling approach to evaluate toxicity-attenuated chemical composition in combination of ginseng and Radix Aconiti Praeparata. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica. 2011;46(12):1488–1492. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

