Somatosensory Nerve Fibers Mediated Generation of De-qi in Manual Acupuncture and Local Moxibustion-Like Stimuli-Modulated Gastric Motility in Rats
- PMID: 24876876
- PMCID: PMC4021835
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/673239
Somatosensory Nerve Fibers Mediated Generation of De-qi in Manual Acupuncture and Local Moxibustion-Like Stimuli-Modulated Gastric Motility in Rats
Abstract
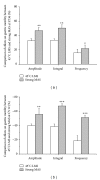
The aim of this study was to reveal the somatosensory nerve fibers mediated generation of De-qi in manual acupuncture stimuli (MAS) and local moxibustion-like stimuli (LMS). The effects of strong and slight MAS, as well as 41°C, 43°C, and 45°C LMS at ST36 and CV12 on gastric motility were observed in rats. Gastric motility was continuously measured by an intrapyloric balloon, and the average amplitude, integral, and frequency of gastric motility during LMS were compared with those of background activity. Gastric motility was facilitated by MAS and LMS at ST36 and inhibited at CV12. The modulatory effects induced by strong MA with potent De-qi (needle grasp feeling) were markedly higher than those by slight MA with mild De-qi sensation (P < 0.05). The nociceptive 43°C and 45°C LMS, rather than nonnociceptive 41°C LMS, produced significant regulatory effects on gastric motility. Based on the afferent fibers activated in the present study, these results support the hypothesis that A δ - and C-afferent fibers were more likely to be involved in the generation of De-qi sensation.
Figures
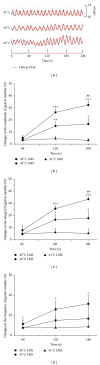
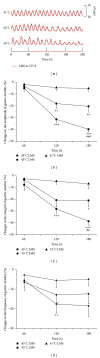
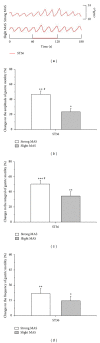
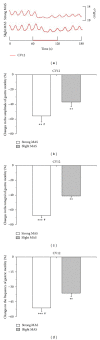
Similar articles
-
Effects of Different Local Moxibustion-Like Stimuli at Zusanli (ST36) and Zhongwan (CV12) on Gastric Motility and Its Underlying Receptor Mechanism.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015;2015:486963. doi: 10.1155/2015/486963. Epub 2015 Jul 12. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015. PMID: 26246837 Free PMC article.
-
Gentle Manual Acupuncture Could Better Regulate Gastric Motility and Vagal Afferent Nerve Discharge of Rats with Gastric Hypomotility.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019 Oct 24;2019:9043151. doi: 10.1155/2019/9043151. eCollection 2019. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019. PMID: 31781283 Free PMC article.
-
"Intensity-response" effects of electroacupuncture on gastric motility and its underlying peripheral neural mechanism.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013;2013:535742. doi: 10.1155/2013/535742. Epub 2013 Jul 1. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013. PMID: 23935667 Free PMC article.
-
[Progress of researches on mechanisms of needling and moxibustion sensations and their related sensation transmission].Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2019 Apr 25;44(4):307-11. doi: 10.13702/j.1000-0607.180043. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2019. PMID: 31056887 Review. Chinese.
-
A literature review of de qi in clinical studies.Acupunct Med. 2013 Jun;31(2):132-42. doi: 10.1136/acupmed-2012-010279. Epub 2013 Mar 13. Acupunct Med. 2013. PMID: 23486017 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Involvement of Neuropeptide Y within Paraventricular Nucleus in Electroacupuncture Inhibiting Sympathetic Activities in Hypertensive Rats.Int J Hypertens. 2022 Jan 18;2022:9990854. doi: 10.1155/2022/9990854. eCollection 2022. Int J Hypertens. 2022. PMID: 35087687 Free PMC article.
-
Acupuncture and regulation of gastrointestinal function.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Jul 21;21(27):8304-13. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i27.8304. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 26217082 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of Different Dosages of ST36 Indirect Moxibustion on the Skin Temperature of the Lower Legs and Feet.Medicines (Basel). 2018 Jun 15;5(2):57. doi: 10.3390/medicines5020057. Medicines (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29914073 Free PMC article.
-
Effects and mechanisms of acupuncture analgesia mediated by afferent nerves in acupoint microenvironments.Front Neurosci. 2024 Feb 7;17:1239839. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1239839. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38384495 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Three Needling Manipulations of Zusanli (ST 36) on Deqi Sensations and Surface Myoelectricity in Healthy Participants.Chin J Integr Med. 2021 Feb;27(2):91-97. doi: 10.1007/s11655-020-3198-0. Epub 2020 May 9. Chin J Integr Med. 2021. PMID: 32388822 Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Tabosa A, Yamamura Y, Romão Forno E, Mello LEAM. A comparative study of the effects of electroacupuncture and moxibustion in the gastrointestinal motility of the rat. Digestive Diseases and Sciences. 2004;49(4):602–610. - PubMed
-
- Sato A, Sato Y, Suzuki A, Uchida S. Neural mechanisms of the reflex inhibition and excitation of gastric motility elicited by acupuncture-like stimulation in anesthetized rats. Neuroscience Research. 1993;18(1):53–62. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

