Cecropia pachystachya: a species with expressive in vivo topical anti-inflammatory and in vitro antioxidant effects
- PMID: 24877079
- PMCID: PMC4022158
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/301294
Cecropia pachystachya: a species with expressive in vivo topical anti-inflammatory and in vitro antioxidant effects
Abstract
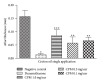
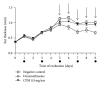
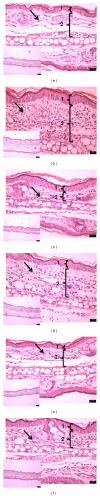
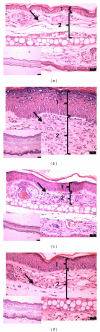
Cecropia pachystachya is a species traditionally used in Brazil to treat inflammation. This work aims to evaluate the topical anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities of the methanolic extract of C. pachystachya (CPM) and to perform its chemical fingerprint by HPLC-DAD. The topical anti-inflammatory activity was evaluated using the mouse models of acute ear inflammation induced by croton oil, arachidonic acid, capsaicin, EPP, phenol, and chronic inflammation induced by multiple application of croton oil. The in vitro antioxidant effect of CPM was investigated using DPPH, reducing power, β -carotene bleaching, and TBARS assays. HPLC analysis was performed to quantify the antioxidant phenolics orientin, isoorientin, and chlorogenic acid previously identified in CPM. CPM exhibited significant anti-inflammatory effect in the acute models, in some cases comparable to the reference drugs. Histopathological analysis showed a moderate chronic skin anti-inflammatory effect with decrease in vasodilation, edema, cell infiltration, and epidermal hyperproliferation. It also showed strong in vitro antioxidant activity. The contents of orientin, isoorientin, and chlorogenic acid were 66.5 ± 1.8, 118.8 ± 0.7, and 5.4 ± 0.2 µg/mg extract, respectively. The topical anti-inflammatory activity of CPM could be based on its antioxidant properties, although other effects are probably involved, including COX inhibition and other mechanisms.
Figures





References
-
- Emre S, Metin A, Demirseren DD, et al. The association of oxidative stress and disease activity in seborrheic dermatitis. Archives of Dermatological Research. 2012;304:683–687. - PubMed
-
- Zhou Q, Mrowietz U, Rostami-Yazdi M. Oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of psoriasis. Free Radical Biology and Medicine. 2009;47(7):891–905. - PubMed
-
- Perry EK, Pickering AT, Wang WW, Houghton PJ, Perry NSL. Medicinal plants and Alzheimer’s disease: from ethnobotany to phytotherapy. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology. 1999;51(5):527–534. - PubMed
-
- Repetto MG, Llesuy SF. Antioxidant properties of natural compounds used in popular medicine for gastric ulcers. Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research. 2002;35(5):523–534. - PubMed
-
- Lorenzi H, Matos FJA. Plantas Medicinais do Brasil. 1st edition. São Paulo, Brazil: Nova Odessa. Instituto Plantarum; 2002.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

