Serum C-reactive protein and procalcitonin kinetics in patients undergoing elective total hip arthroplasty
- PMID: 24877114
- PMCID: PMC4026950
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/565080
Serum C-reactive protein and procalcitonin kinetics in patients undergoing elective total hip arthroplasty
Abstract
Background: The sensitivity and the specificity of different methods to detect periprosthetic infection have been questioned. The current study aimed to investigate the kinetics of C-reactive protein (CRP) and procalcitonin (PCT) in patients undergoing uncomplicated elective total hip arthroplasty (THA), to provide a better interpretation of their levels in noninfectious inflammatory reaction.
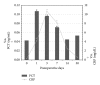
Methods: A total of 51 patients were included. Serum CRP and PCT concentrations were obtained before surgery, on the 1st, 3rd, and 7th postoperative days and after discharge on the 14th and 30th days and at 2 years.
Results: Both markers were confirmed to increase after surgery. The serum CRP showed a marked increase on the 3rd postoperative day while the peak of serum PCT was earlier, even if much lower, on the first day. Then, they declined slowly approaching the baseline values by the second postoperative week. PCT mean values never exceed concentrations typically related to bacterial infections.
Conclusions: CRP is very sensitive to inflammation. It could be the routine screening test in the follow-up of THA orthopaedic patients, but it should be complemented by PCT when there is the clinical suspicion of periprosthetic infection.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of procalcitonin and C-reactive protein for the diagnosis of periprosthetic joint infection before revision total hip arthroplasty.Surg Infect (Larchmt). 2015 Apr;16(2):146-50. doi: 10.1089/sur.2014.034. Epub 2015 Feb 6. Surg Infect (Larchmt). 2015. PMID: 25658716
-
Kinetics of changes in serum concentrations of procalcitonin, interleukin-6, and C- reactive protein after elective abdominal surgery. Can it be used to detect postoperative complications?Coll Antropol. 2013 Mar;37(1):195-201. Coll Antropol. 2013. PMID: 23697273
-
Early serum procalcitonin level after primary total hip replacement.Mediators Inflamm. 2013;2013:927636. doi: 10.1155/2013/927636. Epub 2013 May 13. Mediators Inflamm. 2013. PMID: 23766566 Free PMC article.
-
Usefulness of procalcitonin for diagnosis of infection in cardiac surgical patients.Crit Care Med. 2000 Sep;28(9):3171-6. doi: 10.1097/00003246-200009000-00008. Crit Care Med. 2000. PMID: 11008977
-
Changes in serum procalcitonin, interleukin 6, interleukin 8 and C-reactive protein in neonates after surgery.Eur J Pediatr Surg. 2010 Jul;20(4):262-6. doi: 10.1055/s-0030-1253358. Epub 2010 May 3. Eur J Pediatr Surg. 2010. PMID: 20440673
Cited by
-
Metabolic Shock in Elderly Pertrochanteric or Intertrochanteric Surgery. Comparison of Three Surgical Methods. Is there a Much Safer?Rom J Anaesth Intensive Care. 2020 Dec;27(2):17-26. doi: 10.2478/rjaic-2020-0016. Epub 2020 Dec 31. Rom J Anaesth Intensive Care. 2020. PMID: 34056129 Free PMC article.
-
What Is the Normal Trajectory of C-Reactive Protein, Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate, Plasma Fibrinogen and D-Dimer after Two-Stage Exchange for Periprosthetic Joint Infection?Orthop Surg. 2022 Nov;14(11):2987-2994. doi: 10.1111/os.13533. Epub 2022 Oct 4. Orthop Surg. 2022. PMID: 36193876 Free PMC article.
-
A Broad-Spectrum Infection Diagnostic that Detects Pathogen-Associated Molecular Patterns (PAMPs) in Whole Blood.EBioMedicine. 2016 Jul;9:217-227. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2016.06.014. Epub 2016 Jun 13. EBioMedicine. 2016. PMID: 27333027 Free PMC article.
-
Postoperative Trends of Serum C-Reactive Protein Levels after Primary Shoulder Arthroplasty-Normal Trajectory and Influencing Factors.J Clin Med. 2020 Nov 30;9(12):3893. doi: 10.3390/jcm9123893. J Clin Med. 2020. PMID: 33266181 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamics of C-reactive protein level after orthopedic surgeries.J Orthop. 2023 Nov 13;47:1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jor.2023.11.014. eCollection 2024 Jan. J Orthop. 2023. PMID: 38046451 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Choong PFM, Dowsey MM, Carr D, Daffy J, Stanley P. Risk factors associated with acute hip prosthetic joint infections and outcome of treatment with a rifampinbased regimen. Acta Orthopaedica. 2007;78(6):755–765. - PubMed
-
- Phillips JE, Crane TP, Noy M, Elliott TSJ, Grimer RJ. The incidence of deep prosthetic infections in a specialist orthopaedic hospital. A 15-year prospective survey. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery B. 2006;88(7):943–948. - PubMed
-
- Ridker PM. High-sensitivity C-reactive protein: potential adjunct for global risk assessment in the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease. Circulation. 2001;103(13):1813–1818. - PubMed
-
- Tsimikas S, Willerson JT, Ridker PM. C-reactive protein and other emerging blood biomarkers to optimize risk stratification of vulnerable patients. Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 2006;47(8):C19–C31. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous