The role of uric acid in kidney fibrosis: experimental evidences for the causal relationship
- PMID: 24877124
- PMCID: PMC4026934
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/638732
The role of uric acid in kidney fibrosis: experimental evidences for the causal relationship
Abstract
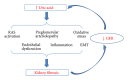
Hyperuricemia is a common finding in chronic kidney disease due to decreased uric acid clearance. The role of uric acid as a risk factor for chronic kidney disease has been largely debated, and recent studies suggested a role of uric acid in the causation and progression of kidney fibrosis, a final common pathway in chronic kidney disease. Uric acid and xanthine oxidase may contribute to kidney fibrosis mainly by inducing inflammation, endothelial dysfunction, oxidative stress, and activation of the renin-angiotensin system. Besides, hyperuricemia induces alterations in renal hemodynamics via afferent arteriolopathy and contributes to the onset and progression of kidney fibrosis. Xanthine oxidase inhibitors may prevent kidney damage via lowering uric acid and/or inhibiting xanthine oxidase. However, there is still no sufficient evidence from interventional clinical researches supporting the causal relationship between uric acid and kidney fibrosis. The effect and role of xanthine oxidase inhibitors in preventing kidney fibrosis and chronic kidney disease progression must be further explored by performing future large scale clinical trials.
Figures

References
-
- Beck LH. Requiem for gouty nephropathy. Kidney International. 1986;30(2):280–287. - PubMed
-
- Filiopoulos V, Hadjiyannakos D, Vlassopoulos D. New insights into uric acid effects on the progression and prognosis of chronic kidney disease. Renal Failure. 2012;34(4):510–520. - PubMed
-
- Kang D-H, Chen W. Uric acid and chronic kidney disease: new understanding of an old problem. Seminars in Nephrology. 2011;31(5):447–452. - PubMed
-
- Badve SV, Brown F, Hawley CM, et al. Challenges of conducting a trial of uric-acid-lowering therapy in CKD. Nature Reviews Nephrology. 2011;7(5):295–300. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

