Guanidino groups greatly enhance the action of antimicrobial peptidomimetics against bacterial cytoplasmic membranes
- PMID: 24878450
- PMCID: PMC4125507
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2014.05.022
Guanidino groups greatly enhance the action of antimicrobial peptidomimetics against bacterial cytoplasmic membranes
Abstract
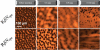
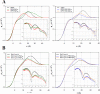
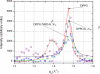
Antimicrobial peptides or their synthetic mimics are a promising class of potential new antibiotics. Herein we assess the effect of the type of cationic side chain (i.e., guanidino vs. amino groups) on the membrane perturbing mechanism of antimicrobial α-peptide-β-peptoid chimeras. Langmuir monolayers composed of 1,2-dipalmitoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphatidylglycerol (DPPG) were used to model cytoplasmic membranes of both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, while lipopolysaccharide Kdo2-lipid A monolayers were mimicking the outer membrane of Gram-negative species. We report the results of the measurements using an array of techniques, including high-resolution synchrotron surface X-ray scattering, epifluorescence microscopy, and in vitro antimicrobial activity to study the molecular mechanisms of peptidomimetic interaction with bacterial membranes. We found guanidino group-containing chimeras to exhibit greater disruptive activity on DPPG monolayers than the amino group-containing analogues. However, this effect was not observed for lipopolysaccharide monolayers where the difference was negligible. Furthermore, the addition of the nitrobenzoxadiazole fluorophore did not reduce the insertion activity of these antimicrobials into both model membrane systems examined, which may be useful for future cellular localization studies.
Keywords: Antimicrobial peptidomimetics; Bacterial membrane; Guanidinium cation; Peptide–peptoid chimeras; Phosphatidylglycerol; X-ray scattering.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
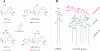

References
-
- Zasloff M. Antimicrobial peptides of multicellular organisms. Nature. 2002;415:389–395. - PubMed
-
- Hancock REW, Sahl HG. Antimicrobial and host-defense peptides as new anti-infective therapeutic strategies. Nature Biotechnology. 2006;24:1551–1557. - PubMed
-
- Fox JL. Antimicrobial peptides stage a comeback. Nature Biotechnology. 2013;31:379–382. - PubMed
-
- Breukink E, Wiedemann I, van Kraaij C, Kuipers OP, Sahl HG, de Kruijff B. Use of the cell wall precursor lipid II by a pore-forming peptide antibiotic. Science. 1999;286:2361–2364. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

