Next-generation sequencing of RNA and DNA isolated from paired fresh-frozen and formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded samples of human cancer and normal tissue
- PMID: 24878701
- PMCID: PMC4039489
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0098187
Next-generation sequencing of RNA and DNA isolated from paired fresh-frozen and formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded samples of human cancer and normal tissue
Abstract
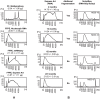
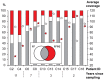
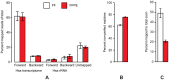
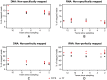
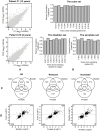
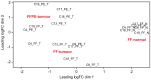
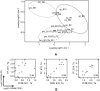
Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tissues are an invaluable resource for clinical research. However, nucleic acids extracted from FFPE tissues are fragmented and chemically modified making them challenging to use in molecular studies. We analysed 23 fresh-frozen (FF), 35 FFPE and 38 paired FF/FFPE specimens, representing six different human tissue types (bladder, prostate and colon carcinoma; liver and colon normal tissue; reactive tonsil) in order to examine the potential use of FFPE samples in next-generation sequencing (NGS) based retrospective and prospective clinical studies. Two methods for DNA and three methods for RNA extraction from FFPE tissues were compared and were found to affect nucleic acid quantity and quality. DNA and RNA from selected FFPE and paired FF/FFPE specimens were used for exome and transcriptome analysis. Preparations of DNA Exome-Seq libraries was more challenging (29.5% success) than that of RNA-Seq libraries, presumably because of modifications to FFPE tissue-derived DNA. Libraries could still be prepared from RNA isolated from two-decade old FFPE tissues. Data were analysed using the CLC Bio Genomics Workbench and revealed systematic differences between FF and FFPE tissue-derived nucleic acid libraries. In spite of this, pairwise analysis of DNA Exome-Seq data showed concordance for 70-80% of variants in FF and FFPE samples stored for fewer than three years. RNA-Seq data showed high correlation of expression profiles in FF/FFPE pairs (Pearson Correlations of 0.90 +/- 0.05), irrespective of storage time (up to 244 months) and tissue type. A common set of 1,494 genes was identified with expression profiles that were significantly different between paired FF and FFPE samples irrespective of tissue type. Our results are promising and suggest that NGS can be used to study FFPE specimens in both prospective and retrospective archive-based studies in which FF specimens are not available.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Wood HM, Belvedere O, Conway C, Daly C, Chalkley R, et al. (2010) Using next-generation sequencing for high resolution multiplex analysis of copy number variation from nanogram quantities of DNA from formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded specimens. Nucleic Acids Res 38: e151 gkq510 [pii]; 10.1093/nar/gkq510 [doi] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kerick M, Isau M, Timmermann B, Sultmann H, Herwig R, et al. (2011) Targeted high throughput sequencing in clinical cancer settings: formaldehyde fixed-paraffin embedded (FFPE) tumor tissues, input amount and tumor heterogeneity. BMC Med Genomics 4: 68 1755-8794-4-68 [pii]; 10.1186/1755-8794-4-68 [doi] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tuononen K, Maki-Nevala S, Sarhadi VK, Wirtanen A, Ronty M, et al. (2013) Comparison of targeted next-generation sequencing (NGS) and real-time PCR in the detection of EGFR, KRAS, and BRAF mutations on formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tumor material of non-small cell lung carcinoma-superiority of NGS. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 52: 503–511 10.1002/gcc.22047 [doi] - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

