Univariate and multivariate analyses of preoperative factors influencing symptomatic outcomes of transoral fundoplication
- PMID: 24879134
- PMCID: PMC4186971
- DOI: 10.1007/s00464-014-3557-z
Univariate and multivariate analyses of preoperative factors influencing symptomatic outcomes of transoral fundoplication
Abstract
Background: Preoperative factors predicting symptomatic improvement after transoral fundoplication (TF) in chronic gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) patients with persistent symptoms on proton-pump inhibitors (PPIs) therapy have not been elucidated fully.
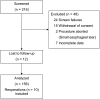
Methods: Univariate and multivariate logistic regression analyses were performed on data from 158 consecutive patients who underwent TF with the EsophyX device between January 2010 and June 2012 in 14 community centers. Variables included age, gender, body mass index, GERD duration, PPIs therapy duration, presence of hiatal hernia, esophagitis, Hill grade, quality of life scores (QOL) on PPIs, % total time pH < 4, and DeMeester score on reflux testing off PPIs.
Results: All patients suffered from typical GERD symptoms. Additionally, 78% (124/158) of patients suffered from atypical symptoms. Six percent (10/158) with recurrent GERD symptoms refractory to PPI therapy underwent revisional procedure (9 laparoscopic Nissen, 1 TF). Median follow-up was 22 (range 10-43) months. For patients with typical symptoms, univariate analyses revealed 4 preoperative factors predictive of successful outcomes: age ≥ 50 [odds ratio (OR) = 2.4, 95% confidence interval (CI) = 1.2-4.8, p = 0.014], GERD Health-related Quality of Life score (GERD-HRQL) ≥ 15 on PPIs (OR = 6.0, CI = 1.2-29.4, p = 0.026, Reflux Symptom Index score > 13 on PPIs (OR = 2.4, CI = 1.1-5.2, p = 0.027), and Gastroesophageal Reflux Symptom Score ≥ 18 on PPIs (OR = 2.6, CI = 1.2-5.8, p = 0.018). Age and GERD-HRQL score remained significant predictors by multivariate analysis. For patients with atypical symptoms, only GERD-HRQL score ≥ 15 on PPIs (OR = 9.9, CI = 0.9-4.6, p = 0.036) was associated with successful outcomes.
Conclusions: Elevated preoperative QOL scores on PPIs and age ≥ 50 were most closely associated with successful outcome of TF in patients with persistent symptoms despite medical therapy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Transoral fundoplication offers durable symptom control for chronic GERD: 3-year report from the TEMPO randomized trial with a crossover arm.Surg Endosc. 2017 Jun;31(6):2498-2508. doi: 10.1007/s00464-016-5252-8. Epub 2016 Sep 21. Surg Endosc. 2017. PMID: 27655380 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Long-term benefit of transoral incisionless fundoplication using the esophyx device for the management of gastroesophageal reflux disease responsive to medical therapy.Dis Esophagus. 2017 Feb 1;30(3):1-8. doi: 10.1111/dote.12525. Dis Esophagus. 2017. PMID: 27868281
-
Efficacy of transoral fundoplication for treatment of chronic gastroesophageal reflux disease incompletely controlled with high-dose proton-pump inhibitors therapy: a randomized, multicenter, open label, crossover study.BMC Gastroenterol. 2014 Oct 6;14:174. doi: 10.1186/1471-230X-14-174. BMC Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25284142 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy of transoral incisionless fundoplication for refractory gastroesophageal reflux disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Endoscopy. 2018 Jul;50(7):708-725. doi: 10.1055/a-0576-6589. Epub 2018 Apr 6. Endoscopy. 2018. PMID: 29625507
-
Effectiveness of laparoscopic fundoplication in relieving the symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and eliminating antireflux medical therapy.Surg Endosc. 2003 Aug;17(8):1200-5. doi: 10.1007/s00464-002-8910-y. Epub 2003 May 13. Surg Endosc. 2003. PMID: 12739117 Review.
Cited by
-
Long-term efficacy of transoral incisionless fundoplication with Esophyx (Tif 2.0) and factors affecting outcomes in GERD patients followed for up to 6 years: a prospective single-center study.Surg Endosc. 2015 Sep;29(9):2770-80. doi: 10.1007/s00464-014-4008-6. Epub 2014 Dec 6. Surg Endosc. 2015. PMID: 25480624
-
Therapeutic Management of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)-Is There Something Between PPI and Fundoplication? An Overview.J Clin Med. 2025 Jan 9;14(2):362. doi: 10.3390/jcm14020362. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 39860368 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endoscopic Management of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: Revisited.Clin Endosc. 2016 Sep;49(5):408-416. doi: 10.5946/ce.2016.133. Epub 2016 Sep 30. Clin Endosc. 2016. PMID: 27744659 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transoral incisionless fundoplication for gastro-esophageal reflux disease: Techniques and outcomes.World J Gastrointest Pharmacol Ther. 2016 May 6;7(2):179-89. doi: 10.4292/wjgpt.v7.i2.179. World J Gastrointest Pharmacol Ther. 2016. PMID: 27158533 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transoral incisionless fundoplication with EsophyX for gastroesophageal reflux disease: clinical efficacy is maintained up to 10 years.Endosc Int Open. 2019 May;7(5):E647-E654. doi: 10.1055/a-0820-2297. Epub 2019 May 2. Endosc Int Open. 2019. PMID: 31058207 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous