The role of GABARAPL1/GEC1 in autophagic flux and mitochondrial quality control in MDA-MB-436 breast cancer cells
- PMID: 24879149
- PMCID: PMC4091181
- DOI: 10.4161/auto.28390
The role of GABARAPL1/GEC1 in autophagic flux and mitochondrial quality control in MDA-MB-436 breast cancer cells
Erratum in
-
Correction.Autophagy. 2019 Oct;15(10):1857. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2019.1639958. Epub 2019 Jul 6. Autophagy. 2019. PMID: 31280645 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
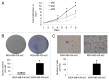
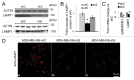
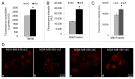
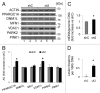
GABARAPL1/GEC1 is an early estrogen-induced gene which encodes a protein highly conserved from C. elegans to humans. Overexpressed GABARAPL1 interacts with GABAA or kappa opioid receptors, associates with autophagic vesicles, and inhibits breast cancer cell proliferation. However, the function of endogenous GABARAPL1 has not been extensively studied. We hypothesized that GABARAPL1 is required for maintaining normal autophagic flux, and plays an important role in regulating cellular bioenergetics and metabolism. To test this hypothesis, we knocked down GABARAPL1 expression in the breast cancer MDA-MB-436 cell line by shRNA. Decreased expression of GABARAPL1 activated procancer responses of the MDA-MB-436 cells including increased proliferation, colony formation, and invasion. In addition, cells with decreased expression of GABARAPL1 exhibited attenuated autophagic flux and a decreased number of lysosomes. Moreover, decreased GABARAPL1 expression led to cellular bioenergetic changes including increased basal oxygen consumption rate, increased intracellular ATP, increased total glutathione, and an accumulation of damaged mitochondria. Taken together, our results demonstrate that GABARAPL1 plays an important role in cell proliferation, invasion, and autophagic flux, as well as in mitochondrial homeostasis and cellular metabolic programs.
Keywords: GABARAP; GABARAPL1; GEC1; LAMP1; LC3; MDA-MB-436; autophagy; breast cancer; lysosome; mitochondria; mitophagy.
Figures






References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
