The Index-based Subgraph Matching Algorithm with General Symmetries (ISMAGS): exploiting symmetry for faster subgraph enumeration
- PMID: 24879305
- PMCID: PMC4039476
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0097896
The Index-based Subgraph Matching Algorithm with General Symmetries (ISMAGS): exploiting symmetry for faster subgraph enumeration
Abstract
Subgraph matching algorithms are used to find and enumerate specific interconnection structures in networks. By enumerating these specific structures/subgraphs, the fundamental properties of the network can be derived. More specifically in biological networks, subgraph matching algorithms are used to discover network motifs, specific patterns occurring more often than expected by chance. Finding these network motifs yields information on the underlying biological relations modelled by the network. In this work, we present the Index-based Subgraph Matching Algorithm with General Symmetries (ISMAGS), an improved version of the Index-based Subgraph Matching Algorithm (ISMA). ISMA quickly finds all instances of a predefined motif in a network by intelligently exploring the search space and taking into account easily identifiable symmetric structures. However, more complex symmetries (possibly involving switching multiple nodes) are not taken into account, resulting in superfluous output. ISMAGS overcomes this problem by using a customised symmetry analysis phase to detect all symmetric structures in the network motif subgraphs. These structures are then converted to symmetry-breaking constraints used to prune the search space and speed up calculations. The performance of the algorithm was tested on several types of networks (biological, social and computer networks) for various subgraphs with a varying degree of symmetry. For subgraphs with complex (multi-node) symmetric structures, high speed-up factors are obtained as the search space is pruned by the symmetry-breaking constraints. For subgraphs with no or simple symmetric structures, ISMAGS still reduces computation times by optimising set operations. Moreover, the calculated list of subgraph instances is minimal as it contains no instances that differ by only a subgraph symmetry. An implementation of the algorithm is freely available at https://github.com/mhoubraken/ISMAGS.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

 is switched with node
is switched with node  and node
and node  with node
with node  . While the G4 graph has no symmetric properties, the tetrahedron and the Petersen graph have more complex symmetric structures.
. While the G4 graph has no symmetric properties, the tetrahedron and the Petersen graph have more complex symmetric structures.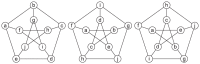
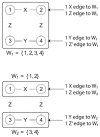
 and
and  have an outgoing
have an outgoing  edge while nodes 3 and 4 do not. This indicates the partition needs to be refined. Nodes
edge while nodes 3 and 4 do not. This indicates the partition needs to be refined. Nodes  and
and  are put in a separate cell as shown in the bottom figure.
are put in a separate cell as shown in the bottom figure.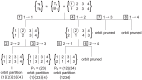
 and
and  . The first coupling
. The first coupling  splits up the cells in both partitions in 3 cells (separation of cells denoted by |). When a permutation is found, the orbit partition is updated as shown. Orbit pruning is used to reduce the required computations as explained in text.
splits up the cells in both partitions in 3 cells (separation of cells denoted by |). When a permutation is found, the orbit partition is updated as shown. Orbit pruning is used to reduce the required computations as explained in text.Similar articles
-
The index-based subgraph matching algorithm (ISMA): fast subgraph enumeration in large networks using optimized search trees.PLoS One. 2013 Apr 19;8(4):e61183. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0061183. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23620730 Free PMC article.
-
A Cytoscape app for motif enumeration with ISMAGS.Bioinformatics. 2017 Feb 1;33(3):461-463. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btw626. Bioinformatics. 2017. PMID: 28158465
-
A linear delay algorithm for enumerating all connected induced subgraphs.BMC Bioinformatics. 2019 Jun 20;20(Suppl 12):319. doi: 10.1186/s12859-019-2837-y. BMC Bioinformatics. 2019. PMID: 31216984 Free PMC article.
-
Grasping frequent subgraph mining for bioinformatics applications.BioData Min. 2018 Sep 3;11:20. doi: 10.1186/s13040-018-0181-9. eCollection 2018. BioData Min. 2018. PMID: 30202444 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Accurate lattice parameters from 2D-periodic images for subsequent Bravais lattice type assignments.Adv Struct Chem Imaging. 2018;4(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s40679-018-0051-z. Epub 2018 Mar 28. Adv Struct Chem Imaging. 2018. PMID: 29607290 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular Graph Generation by Decomposition and Reassembling.ACS Omega. 2023 May 23;8(22):19575-19586. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c01078. eCollection 2023 Jun 6. ACS Omega. 2023. PMID: 37305268 Free PMC article.
-
An Algorithm to Automatically Generate the Combinatorial Orbit Counting Equations.PLoS One. 2016 Jan 21;11(1):e0147078. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0147078. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26797021 Free PMC article.
-
SUBATOMIC: a SUbgraph BAsed mulTi-OMIcs clustering framework to analyze integrated multi-edge networks.BMC Bioinformatics. 2022 Sep 5;23(1):363. doi: 10.1186/s12859-022-04908-3. BMC Bioinformatics. 2022. PMID: 36064320 Free PMC article.
-
Generating random graphs with prescribed graphlet frequency bounds derived from probabilistic networks.PLoS One. 2025 Aug 26;20(8):e0328639. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0328639. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40857227 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Milo R, Shen-Orr S, Itzkovitz S, Kashtan N, Chklovskii D, et al. (2002) Network motifs: simple building blocks of complex networks. Science (New York, NY) 298: 824–827. - PubMed
-
- Kashtan N, Itzkovitz S, Milo R, Alon U (2002) Mfinder tool guide. Technical report, Department of Molecular Cell Biology and Computer Science and Applied Mathematics, Weizman Institute of Science, Israel.
-
- Wernicke S, Rasche F (2006) FANMOD: a tool for fast network motif detection. Bioinformatics (Oxford, England) 22: 1152–3. - PubMed
-
- Wernicke S (2005) A faster algorithm for detecting network motifs. In: Algorithms in Bioinformatics, Springer. pp. 165–177.
-
- McKay BD (1981) Practical graph isomorphism. Department of Computer Science, Vanderbilt University.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

