Visual control of an action discrimination in pigeons
- PMID: 24879863
- PMCID: PMC4144877
- DOI: 10.1167/14.5.16
Visual control of an action discrimination in pigeons
Abstract
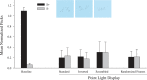
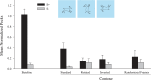
Recognizing and categorizing behavior is essential for all animals. The visual and cognitive mechanisms underlying such action discriminations are not well understood, especially in nonhuman animals. To identify the visual bases of action discriminations, four pigeons were tested in a go/no-go procedure to examine the contribution of different visual features in a discrimination of walking and running actions by different digital animal models. Two different tests with point-light displays derived from studies of human biological motion failed to support transfer of the learned action discrimination from fully figured models. Tests with silhouettes, contours, and the selective deletion or occlusion of different parts of the models indicated that information about the global motions of the entire model was critical to the discrimination. This outcome, along with earlier results, suggests that the pigeons’ discrimination of these locomotive actions involved a generalized categorization of the sequence of configural poses. Because the motor systems for locomotion and flying in pigeons share little in common with quadruped motions, the pigeons’ discrimination of these behaviors creates problems for motor theories of action recognition based on mirror neurons or related notions of embodied cognition. It suggests instead that more general motion and shape mechanisms are sufficient for making such discriminations, at least in birds.
Keywords: action recognition; biological motion; global perception; occlusion; pigeon.
© 2014 ARVO.
Figures




References
-
- Aggarwal J. K., Cai Q. (1999). Human motion analysis: A review. Computer Vision and Image Understanding , 73, 428–440
-
- Arbib M. A. (2005). From monkey-like action recognition to human language: An evolutionary framework for neurolinguistics. Behavioral and Brain Sciences , 28, 105–124 - PubMed
-
- Asen Y. L., Cook R. G. (2012). Discrimination and categorization of actions by pigeons. Psychological Science , 23, 617–624, doi:10.1177/0956797611433333 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Aust U., Huber L. (2006). Does the use of natural stimuli facilitate amodal completion in pigeons? Perception , 35, 333–349 - PubMed
-
- Beintema J. A., Lappe M. (2002). Perception of biological motion without local image motion. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA , 99 (8), 5661–5663, doi:10.1073/pnas.082483699 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

