GPS-SUMO: a tool for the prediction of sumoylation sites and SUMO-interaction motifs
- PMID: 24880689
- PMCID: PMC4086084
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gku383
GPS-SUMO: a tool for the prediction of sumoylation sites and SUMO-interaction motifs
Abstract
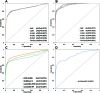
Small ubiquitin-like modifiers (SUMOs) regulate a variety of cellular processes through two distinct mechanisms, including covalent sumoylation and non-covalent SUMO interaction. The complexity of SUMO regulations has greatly hampered the large-scale identification of SUMO substrates or interaction partners on a proteome-wide level. In this work, we developed a new tool called GPS-SUMO for the prediction of both sumoylation sites and SUMO-interaction motifs (SIMs) in proteins. To obtain an accurate performance, a new generation group-based prediction system (GPS) algorithm integrated with Particle Swarm Optimization approach was applied. By critical evaluation and comparison, GPS-SUMO was demonstrated to be substantially superior against other existing tools and methods. With the help of GPS-SUMO, it is now possible to further investigate the relationship between sumoylation and SUMO interaction processes. A web service of GPS-SUMO was implemented in PHP+JavaScript and freely available at http://sumosp.biocuckoo.org.
© The Author(s) 2014. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures
References
-
- Geiss-Friedlander R., Melchior F. Concepts in sumoylation: a decade on. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007;8:947–956. - PubMed
-
- Hay R.T. SUMO: a history of modification. Mol. Cell. 2005;18:1–12. - PubMed
-
- Muller S., Hoege C., Pyrowolakis G., Jentsch S. SUMO, ubiquitin's mysterious cousin. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2001;2:202–210. - PubMed
-
- Seeler J.S., Dejean A. Nuclear and unclear functions of SUMO. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2003;4:690–699. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

