The association between cue-reactivity in the precuneus and level of dependence on nicotine and alcohol
- PMID: 24880692
- PMCID: PMC4166553
- DOI: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2014.04.026
The association between cue-reactivity in the precuneus and level of dependence on nicotine and alcohol
Abstract
Background: Given numerous reports implicating involvement of the precuneus in cue-reactivity paradigms, the goal of this investigation was to examine the relationship between activation of the precuneus in response to drug cues and measures of subjective craving and severity of dependence in volunteers who were comorbid for alcohol and nicotine abuse.
Methods: Forty research participants, who all reported heavy drinking and daily smoking, were recruited (15 women; 70% Caucasian; mean age=31.2 years) for a functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) session involving a cigarette video-cues task and an alcohol taste-cues task. Mean precuneus activation from both tasks during cue presentation was subjected to bivariate correlation analyses with indices of dependence severity and subjective craving.
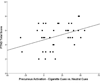
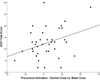
Results: Precuneus activation in the contrast of Cigarette Cues vs. Control Cues was positively correlated with scores on the Fagerström Test of Nicotine Dependence (r=0.389, p=0.016), and activation in the Alcohol Cues vs. Control Cues contrast was positively correlated with Alcohol Dependence Scale scores (r=0.338, p=0.038). No correlations with subjective craving were observed (ps>0.05).
Conclusions: These findings indicate that the precuneus is involved in cue reactivity for both cigarettes and alcohol, and that this involvement is moderated by severity of drug dependence. The precuneus may be a cortical locus for neuroplastic changes related to drug dependence.
Keywords: Alcohol use disorder; Cigarettes; Craving; Cue-reactivity; Precuneus; fMRI.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
LAR is a paid consultant for GSK. All other authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

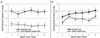
Similar articles
-
Right anterior insula connectivity is important for cue-induced craving in nicotine-dependent smokers.Addict Biol. 2015 Mar;20(2):407-14. doi: 10.1111/adb.12124. Epub 2014 Feb 13. Addict Biol. 2015. PMID: 24529072 Free PMC article.
-
P3 event-related potential reactivity to smoking cues: Relations with craving, tobacco dependence, and alcohol sensitivity in young adult smokers.Psychol Addict Behav. 2017 Feb;31(1):61-72. doi: 10.1037/adb0000233. Epub 2016 Nov 17. Psychol Addict Behav. 2017. PMID: 27854454 Free PMC article.
-
Severity of nicotine dependence modulates cue-induced brain activity in regions involved in motor preparation and imagery.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2006 Mar;184(3-4):577-88. doi: 10.1007/s00213-005-0080-x. Epub 2005 Aug 13. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2006. PMID: 16133128
-
Differences in Magnitude of Cue Reactivity Across Durations of Smoking History: A Meta-analysis.Nicotine Tob Res. 2020 Jul 16;22(8):1267-1276. doi: 10.1093/ntr/ntz071. Nicotine Tob Res. 2020. PMID: 31050735 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Factors modulating neural reactivity to drug cues in addiction: a survey of human neuroimaging studies.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2014 Jan;38:1-16. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2013.10.013. Epub 2013 Nov 6. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2014. PMID: 24211373 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Altered patterns of fractional amplitude of low-frequency fluctuation and regional homogeneity in abstinent methamphetamine-dependent users.Sci Rep. 2021 Apr 8;11(1):7705. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-87185-z. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33833282 Free PMC article.
-
Dorsal anterior cingulate glutamate is associated with engagement of the default mode network during exposure to smoking cues.Drug Alcohol Depend. 2016 Oct 1;167:75-81. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2016.07.021. Epub 2016 Aug 9. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2016. PMID: 27522872 Free PMC article.
-
Neural correlates of the addictions neuroclinical assessment (ANA) incentive salience factor among individuals with alcohol use disorder.Behav Brain Res. 2024 Apr 27;464:114926. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2024.114926. Epub 2024 Feb 29. Behav Brain Res. 2024. PMID: 38431152 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying neural signatures of tobacco retail outlet exposure: Preliminary validation of a "community neuroscience" paradigm.Addict Biol. 2021 Sep;26(5):e13029. doi: 10.1111/adb.13029. Epub 2021 Mar 4. Addict Biol. 2021. PMID: 33663023 Free PMC article.
-
Delta coherence in resting-state EEG predicts the reduction in cigarette craving after hypnotic aversion suggestions.Sci Rep. 2017 May 25;7(1):2430. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-01373-4. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28546584 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. Arlington, VA: American Psychiatric Publishing; 2013.
-
- Andersson J, Jenkinson M, Smith S. Non-linear Registration. FMRIB Technical report TR07JA2. 2007
-
- Beck AT, Steer RA, Brown G. Manual for the Beck Depression Inventory-II. San Antonio, TX: Psychological Corporation; 1996.
-
- Bonson KR, Grant SJ, Contoreggi CS, Links JM, Metcalfe J, Weyl HL, Kurian V, Ernst M, London ED. Neural systems and cue-induced cocaine craving. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2002;26:376–386. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

