[Lactoferrin downregulates the expression of toll like receptor 4 stimulated by lipopolysaccharide in human periodontal ligament cells]
- PMID: 24881213
- PMCID: PMC7030810
- DOI: 10.7518/hxkq.2014.02.014
[Lactoferrin downregulates the expression of toll like receptor 4 stimulated by lipopolysaccharide in human periodontal ligament cells]
Abstract
Objective: To examine the role of lactoferrin (LF) on Toll like receptor 4 (TLR4) stimulated by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in human periodontal ligament cells (hPDLCs).
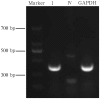
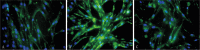
Methods: Primary hPDLCs were cultured by tissue block enzymolytic method. Cells obtained from four passages were identified and used in this experiment. Cells without stimulation served as the controls and cells treated with LPS (0.1 microg x mL(-1)) comprised the LPS group. The LPS + LF group was pretreated with LPS (0.1 microg x mL(-1)) for 2 h, and then treated with LF (10 microg x mL(-1)). Four hours after LF stimulation, the mRNA expression levels of TLR4 were examined by real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). The protein expression of TLR4 was observed by cell immunofluorescence staining after LF stimulation of 24 hours.
Results: TLR4 mRNA expression in the LPS + LF group was significantly more decreased than that in the LPS group (P < 0.05), but exhibited no difference with that in the control group (P > 0.05). Cell immunofluorescence staining showed that the protein expression of TLR4 in the LPS + LF group was significantly more decreased than that in the LPS group (P < 0.05), but exhibited no difference with that in the control group (P > 0.05).
Conclusion: LF can decrease the expression of TLR4 stimulated by LPS in hPDLCs, thus presenting potential application for controlling the TLR4 immune pathway of periodontitis.
目的: 观察乳铁蛋白(LF)对经脂多糖(LPS)刺激的人牙周膜细胞(hPDLCs)表达Toll样受体4(TLR4)的影响。
方法: 采用组织块酶消化法培养hPDLCs,鉴定后取第4代细胞,分成空白对照组、LPS组、LPS+LF组。空白对照组不加任何刺激,LPS组加入0.1 µg·mL−1 LPS;LPS+LF组在加入0.1 µg·mL−1 LPS 2 h后,加入10 µg·mL−1 LF。以加入LF时开始计算时间,4 h后采用实时定量聚合酶链反应(RT-PCR)法检测hPDLCs中TLR4 mRNA的表达,24 h后采用细胞免疫荧光染色法观察TLR4蛋白的表达。
结果: RT-PCR检测显示:LPS+LF组TLR4 mRNA表达较LPS组明显降低(P<0.05),与空白对照组无明显差异(P>0.05)。细胞免疫荧光染色法显示:LPS+LF组TLR4蛋白的表达强度较LPS组减弱(P<0.05),与空白对照组无明显差别(P>0.05)。
结论: LF可以下调LPS激发的hPDLCs中TLR4的表达,在牙周炎症TLR4信号通路的调控过程中有一定的作用。
Figures
References
-
- Tang L, Zhou XD, Wang Q, et al. Expression of TRAF6 and pro-inflammatory cytokines through activation of TLR2, TLR4, NOD1, and NOD2 in human periodontal ligament fibroblasts[J] Arch Oral Biol. 2011;56(10):1064–1072. - PubMed
-
- Pecorini C, Sassera D, Rebucci R, et al. Evaluation of the protective effect of bovine lactoferrin against lipopolysaccharides in a bovine mammary epithelial cell line[J] Vet Res Commun. 2010;34(3):267–276. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
