Carboplatin loaded polymethylmethacrylate nano-particles in an adjunctive role in retinoblastoma: an animal trial
- PMID: 24881606
- PMCID: PMC4065510
- DOI: 10.4103/0301-4738.129792
Carboplatin loaded polymethylmethacrylate nano-particles in an adjunctive role in retinoblastoma: an animal trial
Abstract
Purpose: The purpose of the study is to compare the intra-vitreal concentrations of carboplatin, post peri-ocular injections of commercially available carboplatin (CAC) and a novel carboplatin loaded polymethylmethacrylate nanoparticulate carboplatin (NPC), in either eye, as a model system for treatment of advanced intra-ocular retinoblastoma (RB).
Design: Experimental, comparative, animal study.
Materials and methods: Polymethylmethacrylate nanoparticles were prepared by free radical emulsion polymerization of methyl methacrylate in aqueous solution of carboplatin in the presence of surfactant sodium dodecyl sulfate and thermal initiator ammonium persulfate. 21 Sprague-Dawley rats, aged between 6 weeks and 3 months were enrolled. The right eye of each rat was injected peri-ocularly with CAC formulation (1 ml of 10 mg/ml) and the left eye with NPC (1 ml of 10 mg/ml), post-anesthesia, by an ophthalmologist trained in ocular oncology. Three rats each were euthanized on days 1, 3, 5, 7, 14, 28 and 42, post-injection and both eyes were carefully enucleated. Intra-vitreal concentrations of CAC and NPC were determined with Inductively Coupled Plasma Atomic Emission Spectroscopy. Analysis of data was done with paired t-test.
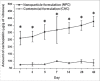
Results: The intra-vitreal concentration of carboplatin with NPC was ~3-4 times higher than with CAC in all animals, on all the days (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: A higher trans-scleral permeability gradient is obtained with the novel nanoparticles than with the commercial drug, leading to sustained higher levels of carboplatin in the vitreous. Peri-ocular injection of NPC could thus have an adjuvant efficacy in the treatment for advanced clinical RB, specifically those with vitreous seeds.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
In vivo intraocular distribution and safety of periocular nanoparticle carboplatin for treatment of advanced retinoblastoma in humans.Am J Ophthalmol. 2014 May;157(5):1109-15. doi: 10.1016/j.ajo.2014.01.027. Epub 2014 Feb 4. Am J Ophthalmol. 2014. PMID: 24503408 Clinical Trial.
-
Does a nanomolecule of Carboplatin injected periocularly help in attaining higher intravitreal concentrations?Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2009 Dec;50(12):5896-900. doi: 10.1167/iovs.09-3914. Epub 2009 Jul 23. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2009. PMID: 19628744
-
Intravitreal carboplatin concentration and area under concentration versus time curve after intravitreal and periocular delivery.Eur J Ophthalmol. 2010 Jul-Aug;20(4):745-51. doi: 10.1177/112067211002000416. Eur J Ophthalmol. 2010. PMID: 20306443
-
Fibrin sealant for retinoblastoma: where are we?J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2008 Oct;24(5):433-8. doi: 10.1089/jop.2007.0110. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2008. PMID: 18788992 Review.
-
OCULAR PHARMACOLOGY OF CHEMOTHERAPY FOR RETINOBLASTOMA.Retina. 2017 Jan;37(1):1-10. doi: 10.1097/IAE.0000000000001275. Retina. 2017. PMID: 27617542 Review.
Cited by
-
Nanotechnology for Pediatric Retinoblastoma Therapy.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Aug 31;15(9):1087. doi: 10.3390/ph15091087. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36145308 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanotechnology in retinal drug delivery.Int J Ophthalmol. 2018 Jun 18;11(6):1038-1044. doi: 10.18240/ijo.2018.06.23. eCollection 2018. Int J Ophthalmol. 2018. PMID: 29977820 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanomedicine-Based Treatments for Rare and Aggressive Ocular Cancers: Advances in Drug Delivery.Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2025 Jul;26(7):569-586. doi: 10.1007/s11864-025-01330-8. Epub 2025 May 22. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40399581 Review.
-
An Update on Emergent Nano-Therapeutic Strategies against Pediatric Brain Tumors.Brain Sci. 2024 Feb 18;14(2):185. doi: 10.3390/brainsci14020185. Brain Sci. 2024. PMID: 38391759 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Shields CL, Honavar SG, Shields JA, Demirci H, Meadows AT, Naduvilath TJ. Factors predictive of recurrence of retinal tumors, vitreous seeds, and subretinal seeds following chemoreduction for retinoblastoma. Arch Ophthalmol. 2002;120:460–4. - PubMed
-
- Shields CL, Shields JA. Recent developments in the management of retinoblastoma. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1999;36:8–18. - PubMed
-
- Murphree AL, Villablanca JG, Deegan WF, 3rd, Sato JK, Malogolowkin M, Fisher A, et al. Chemotherapy plus local treatment in the management of intraocular retinoblastoma. Arch Ophthalmol. 1996;114:1348–56. - PubMed
-
- Shields CL, Shields JA, Needle M, de Potter P, Kheterpal S, Hamada A, et al. Combined chemoreduction and adjuvant treatment for intraocular retinoblastoma. Ophthalmology. 1997;104:2101–11. - PubMed
-
- Dunkel IJ, Lee TC, Shi W, Beaverson KL, Novetsky D, Lyden D, et al. A phase II trial of carboplatin for intraocular retinoblastoma. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2007;49:643–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources