Resveratrol prevents high fat/sucrose diet-induced central arterial wall inflammation and stiffening in nonhuman primates
- PMID: 24882067
- PMCID: PMC4254394
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2014.04.018
Resveratrol prevents high fat/sucrose diet-induced central arterial wall inflammation and stiffening in nonhuman primates
Abstract
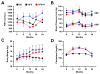
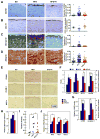
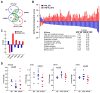
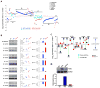
Central arterial wall stiffening, driven by a chronic inflammatory milieu, accompanies arterial diseases, the leading cause of cardiovascular (CV) morbidity and mortality in Western society. An increase in central arterial wall stiffening, measured as an increase in aortic pulse wave velocity (PWV), is a major risk factor for clinical CV disease events. However, no specific therapies to reduce PWV are presently available. In rhesus monkeys, a 2 year diet high in fat and sucrose (HFS) increases not only body weight and cholesterol, but also induces prominent central arterial wall stiffening and increases PWV and inflammation. The observed loss of endothelial cell integrity, lipid and macrophage infiltration, and calcification of the arterial wall were driven by genomic and proteomic signatures of oxidative stress and inflammation. Resveratrol prevented the HFS-induced arterial wall inflammation and the accompanying increase in PWV. Dietary resveratrol may hold promise as a therapy to ameliorate increases in PWV.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest relevant to this article were reported.
Figures
References
-
- Bakker EN, Pistea A, VanBavel E. Transglutaminases in vascular biology: relevance for vascular remodeling and atherosclerosis. J Vasc Res. 2008;45:271–278. - PubMed
-
- Carrizzo A, Puca A, Damato A, Marino M, Franco E, Pompeo F, Traficante A, Civitillo F, Santini L, Trimarco V, et al. Resveratrol improves vascular function in patients with hypertension and dyslipidemia by modulating NO metabolism. Hypertension. 2013;62:359–366. - PubMed
-
- Do GM, Kwon EY, Kim HJ, Jeon SM, Ha TY, Park T, Choi MS. Long-term effects of resveratrol supplementation on suppression of atherogenic lesion formation and cholesterol synthesis in apo E-deficient mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008;374:55–59. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

