Stretch-induced human myometrial cytokines enhance immune cell recruitment via endothelial activation
- PMID: 24882387
- PMCID: PMC4654292
- DOI: 10.1038/cmi.2014.39
Stretch-induced human myometrial cytokines enhance immune cell recruitment via endothelial activation
Abstract
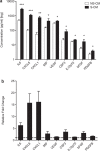
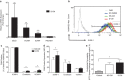
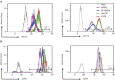
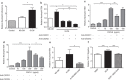
Spontaneous term labour is associated with amplified inflammatory events in the myometrium including cytokine production and leukocyte infiltration; however, potential mechanisms regulating such events are not fully understood. We hypothesized that mechanical stretch of the uterine wall by the growing fetus facilitates peripheral leukocyte extravasation into the term myometrium through the release of various cytokines by uterine myocytes. Human myometrial cells (hTERT-HM) were subjected to static mechanical stretch; stretch-conditioned media was collected and analysed using 48-plex Luminex assay and ELISA. Effect of stretch-conditioned media on cell adhesion molecule expression of human uterine microvascular endothelial cells (UtMVEC-Myo) was detected by quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) and flow cytometry; functional assays testing leukocyte-endothelial interactions: adhesion of leukocytes to endothelial cells and transendothelial migration of calcein-labelled primary human neutrophils as well as migration of THP-1 monocytic cells were assessed by fluorometry. The current in vitro study demonstrated that mechanical stretch (i) directly induces secretion of multiple cytokines and chemokines by hTERT-HM cells (IL-6, CXCL8, CXCL1, migration inhibitory factor (MIF), VEGF, G-CSF, IL-12p70, bFGF and platelet-derived growth factor subunit B (PDGF-bb), P<0.05); stretch-induced cytokines (ii) enhance leukocyte adhesion to the endothelium of the surrounding uterine microvasculature by (iii) inducing the expression of endothelial cell adhesion molecules and (iv) directing the transendothelial migration of peripheral leukocytes. (vi) Chemokine-neutralizing antibodies and broad-spectrum chemokine inhibitor block leukocyte migration. Our data provide a proof of mechanical regulation for leukocyte recruitment from the uterine blood vessels to the myometrium, suggesting a putative mechanism for the leukocyte infiltrate into the uterus during labour and postpartum involution.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Decidual Inflammation Drives Chemokine-Mediated Immune Infiltration Contributing to Term Labor.J Immunol. 2021 Oct 15;207(8):2015-2026. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2100493. Epub 2021 Sep 15. J Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34526377 Free PMC article.
-
RAF1 is increased in labouring myometrium and modulates inflammation-induced pro-labour mediators.Reproduction. 2016 Apr;151(4):411-20. doi: 10.1530/REP-15-0607. Epub 2016 Jan 25. Reproduction. 2016. PMID: 26811545
-
Stretch and inflammatory cytokines drive myometrial chemokine expression via NF-κB activation.Endocrinology. 2012 Jan;153(1):481-91. doi: 10.1210/en.2011-1506. Epub 2011 Nov 1. Endocrinology. 2012. PMID: 22045664
-
Low shear stress up-regulation of proinflammatory gene expression in human retinal microvascular endothelial cells.Exp Eye Res. 2013 Nov;116:308-11. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2013.10.001. Epub 2013 Oct 12. Exp Eye Res. 2013. PMID: 24128656 Review.
-
Integration of endocrine and mechanical signals in the regulation of myometrial functions during pregnancy and labour.Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2009 May;144 Suppl 1:S2-10. doi: 10.1016/j.ejogrb.2009.02.044. Epub 2009 Mar 18. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2009. PMID: 19299064 Review.
Cited by
-
Is human labor at term an inflammatory condition?†.Biol Reprod. 2023 Jan 14;108(1):23-40. doi: 10.1093/biolre/ioac182. Biol Reprod. 2023. PMID: 36173900 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Maternal-Fetal Inflammation in the Placenta and the Developmental Origins of Health and Disease.Front Immunol. 2020 Nov 13;11:531543. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.531543. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33281808 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Crosstalk between monocytes and myometrial smooth muscle in culture generates synergistic pro-inflammatory cytokine production and enhances myocyte contraction, with effects opposed by progesterone.Mol Hum Reprod. 2015 Aug;21(8):672-86. doi: 10.1093/molehr/gav027. Epub 2015 May 22. Mol Hum Reprod. 2015. PMID: 26002969 Free PMC article.
-
The frequency and clinical significance of intra-amniotic inflammation in twin pregnancies with preterm labor and intact membranes.J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2019 Feb;32(4):527-541. doi: 10.1080/14767058.2017.1384460. Epub 2017 Oct 11. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2019. PMID: 29020827 Free PMC article.
-
Piezo1 overexpression in the uterus contributes to myometrium contraction and inflammation-associated preterm birth.J Transl Med. 2024 Dec 23;22(1):1140. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05978-y. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 39716206 Free PMC article.
References
-
- 1Golightly E, Jabbour HN, Norman JE. Endocrine immune interactions in human parturition. Mol Cell Endocrinol 2011; 335: 52–59. - PubMed
-
- 2Unal ER, Cierny JT, Roedner C, Newman R, Goetzl L. Maternal inflammation in spontaneous term labor. Am J Obstetr Gynecol 2011; 204: 223.e1–223.e5. - PubMed
-
- 5Luppi P, Irwin TE, Simhan H, Deloia JA. CD11b expression on circulating leukocytes increases in preparation for parturition. Am J Reprod Immunol 2004; 52: 323–329. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

