Hippo-independent activation of YAP by the GNAQ uveal melanoma oncogene through a trio-regulated rho GTPase signaling circuitry
- PMID: 24882515
- PMCID: PMC4074519
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccr.2014.04.016
Hippo-independent activation of YAP by the GNAQ uveal melanoma oncogene through a trio-regulated rho GTPase signaling circuitry
Abstract
Mutually exclusive activating mutations in the GNAQ and GNA11 oncogenes, encoding heterotrimeric Gαq family members, have been identified in ∼ 83% and ∼ 6% of uveal and skin melanomas, respectively. However, the molecular events underlying these GNAQ-driven malignancies are not yet defined, thus limiting the ability to develop cancer-targeted therapies. Here, we focused on the transcriptional coactivator YAP, a critical component of the Hippo signaling pathway that controls organ size. We found that Gαq stimulates YAP through a Trio-Rho/Rac signaling circuitry promoting actin polymerization, independently of phospholipase Cβ and the canonical Hippo pathway. Furthermore, we show that Gαq promotes the YAP-dependent growth of uveal melanoma cells, thereby identifying YAP as a suitable therapeutic target in uveal melanoma, a GNAQ/GNA11-initiated human malignancy.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
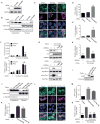
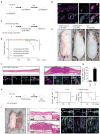
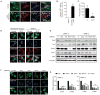
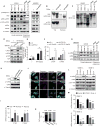

Comment in
-
GNAQ/11 mutations in uveal melanoma: is YAP the key to targeted therapy?Cancer Cell. 2014 Jun 16;25(6):714-5. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2014.05.028. Cancer Cell. 2014. PMID: 24937456 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adler JJ, Johnson DE, Heller BL, Bringman LR, Ranahan WP, Conwell MD, Sun Y, Hudmon A, Wells CD. Serum deprivation inhibits the transcriptional co-activator YAP and cell growth via phosphorylation of the 130-kDa isoform of Angiomotin by the LATS1/2 protein kinases. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2013;110:17368–17373. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aragona M, Panciera T, Manfrin A, Giulitti S, Michielin F, Elvassore N, Dupont S, Piccolo S. A Mechanical Checkpoint Controls Multicellular Growth through YAP/TAZ Regulation by Actin-Processing Factors. Cell. 2013;154:1047–1059. - PubMed
-
- Bar-Sagi D, Hall A. Ras and Rho GTPases: a family reunion. Cell. 2000;103:227–238. - PubMed
-
- Barbazetto IA, Lee TC, Rollins IS, Chang S, Abramson DH. Treatment of choroidal melanoma using photodynamic therapy. Am J Ophthalmol. 2003;135:898–899. - PubMed
-
- Berman DM, Wilkie TM, Gilman AG. GAIP and RGS4 are GTPase-activating proteins for the G(i) subfamily of G protein alpha subunits. Cell. 1996;86:445–452. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

